How to Use SPSS for Predictive Analysis Assignments|2025
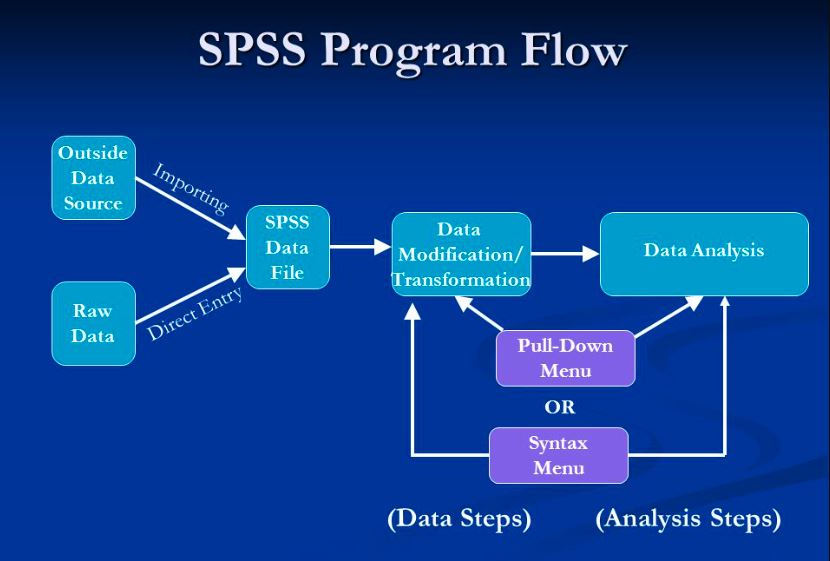
Predictive analysis is a powerful statistical technique that enables analysts to forecast future outcomes based on historical data. IBM SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) is one of the most versatile tools for performing predictive analysis assignments, offering a wide range of features to analyze data, build models, and generate actionable insights. This guide explores how to use SPSS for predictive analysis assignments, providing step-by-step instructions and practical tips.
Why Choose SPSS for Predictive Analysis?
SPSS is a preferred tool for predictive analysis due to its:
- User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive menus and drag-and-drop features make it accessible for beginners.
- Comprehensive Functionality: Includes tools for regression, decision trees, and machine learning algorithms.
- Seamless Data Integration: Works with diverse file formats, including Excel, CSV, and SQL databases.
- Visualization Tools: Offers charts and graphs to enhance data interpretation.
Getting Started with Predictive Analysis in SPSS
1. Define the Objective
Start by defining the goal of your predictive analysis assignment. Common objectives include:
- Predicting customer behavior (e.g., churn, purchase likelihood).
- Forecasting sales or revenue.
- Identifying risk factors in health or finance.
A clear objective helps determine the appropriate data, variables, and analysis techniques.
2. Collect and Prepare Data
Data preparation is critical for accurate predictive analysis. Follow these steps:
- Data Collection:
- Gather historical data relevant to the prediction task.
- Ensure data quality by verifying completeness and consistency.
- Data Cleaning:
- Handle missing values using Transform > Replace Missing Values.
- Remove duplicates and correct inconsistencies.
- Data Transformation:
- Recode categorical variables into numeric formats (Transform > Recode into Different Variables).
- Normalize or standardize continuous variables if required.
- Load Data into SPSS:
- Open the data file in SPSS by selecting File > Open > Data.
3. Explore the Data
Before building predictive models, understand your data using descriptive statistics and visualizations:
- Descriptive Statistics:
- Use Analyze > Descriptive Statistics > Frequencies or Descriptives to compute measures like mean, median, and standard deviation.
- Visualization:
- Create histograms, scatterplots, or boxplots using Graphs > Chart Builder to identify trends and anomalies.
Building Predictive Models in SPSS
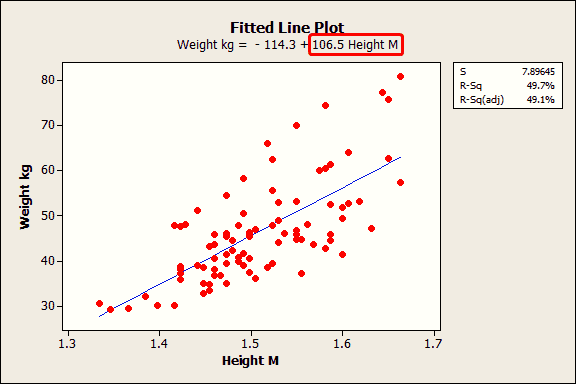
1. Linear Regression
Linear regression predicts a continuous dependent variable based on one or more independent variables. Steps include:
- Go to Analyze > Regression > Linear.
- Select the dependent variable and independent variables.
- Click OK to run the analysis.
- Interpret the coefficients in the output to understand variable impact.
2. Logistic Regression
Logistic regression is used when the dependent variable is binary (e.g., yes/no, 0/1). Steps include:
- Go to Analyze > Regression > Binary Logistic.
- Specify the dependent variable and predictors.
- Review the odds ratios (Exp(B)) in the output to interpret the likelihood of outcomes.
3. Decision Trees
Decision trees classify data into categories or predict outcomes based on splits in the data:
- Navigate to Analyze > Classify > Tree.
- Select the dependent and independent variables.
- Choose a tree-growing method (e.g., CHAID, CART).
- Examine the tree diagram and node statistics for insights.
4. Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis forecasts future values based on historical trends:
- Go to Analyze > Forecasting > Create Models.
- Select the time series variable and model type (e.g., ARIMA, exponential smoothing).
- Review the model fit statistics and predicted values.
5. Neural Networks
Neural networks are advanced machine learning models for complex, non-linear relationships:
- Go to Analyze > Neural Networks > Multilayer Perceptron.
- Specify the dependent and independent variables.
- Customize settings like activation functions and training algorithms.
- Interpret the weights and hidden layer nodes for insights.
Evaluating Predictive Models
1. Assess Model Fit
SPSS provides metrics to evaluate model performance:
- R-Squared: Indicates the proportion of variance explained by the model (higher is better).
- Accuracy: Percentage of correct predictions for classification models.
- Mean Absolute Error (MAE): Average absolute error of predictions (lower is better).
2. Validate the Model
Use cross-validation or a train-test split to ensure model generalizability:
- Split the dataset using Data > Select Cases.
- Build the model on the training set and test it on the validation set.
- Compare performance metrics across datasets.
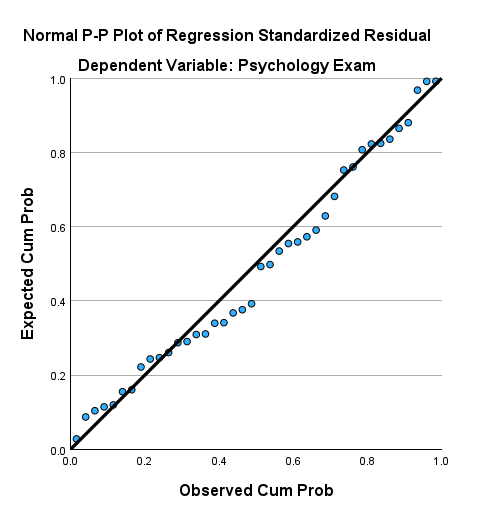
3. Check Assumptions
Ensure the model meets key assumptions:
- Linearity: Relationships between variables should be linear for linear regression.
- Independence: Observations should be independent.
- Normality: Residuals should be normally distributed.
Interpreting Results
1. Relate Findings to Objectives
Interpret results in the context of the research objective. For instance:
- A high R-squared value indicates that the model explains most of the variability in the dependent variable.
- Significant predictors (p < 0.05) provide actionable insights for decision-making.
2. Use Visualizations
SPSS allows you to generate charts and plots for better interpretation:
- Use scatterplots for regression line fit.
- Create classification matrices for logistic regression.
- Visualize decision tree paths.
3. Report Confidence Levels
Include confidence intervals and p-values to communicate the reliability of your predictions.
Advanced Predictive Techniques in SPSS
1. Ensemble Methods
Combine multiple models to improve prediction accuracy. SPSS Modeler supports techniques like bagging and boosting.
2. Text Analytics
Analyze unstructured data (e.g., customer reviews) by integrating SPSS with text analytics tools.
3. Predictive Modeling Extensions
Extend SPSS functionality with Python or R for custom predictive algorithms.
Common Challenges and Solutions
1. Overfitting
- Challenge: The model performs well on training data but poorly on unseen data.
- Solution: Use regularization techniques or simplify the model.
2. Missing Data
- Challenge: Incomplete data can bias predictions.
- Solution: Impute missing values or use robust models.
3. Multicollinearity
- Challenge: Highly correlated predictors distort coefficients.
- Solution: Use variable selection methods or dimensionality reduction.
Applications of Predictive Analysis in SPSS
SPSS is widely used across industries:
- Marketing: Predict customer lifetime value, segment markets.
- Healthcare: Forecast disease progression, evaluate treatment efficacy.
- Finance: Assess credit risk, predict stock prices.
- Education: Predict student performance, optimize resource allocation.
Learning Resources for SPSS Predictive Analysis
- IBM SPSS Tutorials: Official guides and examples.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and edX offer SPSS training.
- Books: Reference texts such as Data Analysis Using SPSS by Darren George.
- Forums and Communities: Join discussions on ResearchGate or SPSS user groups.
Conclusion
Using SPSS for predictive analysis assignments can unlock valuable insights and support data-driven decision-making. By following this guide, you can confidently prepare data, build robust models, and interpret results like a pro. Whether you are forecasting trends, identifying risks, or optimizing strategies, SPSS is a powerful ally in predictive analysis. Getspsshelp.com provides expert guidance on using SPSS for predictive analysis assignments, helping students apply advanced statistical techniques to forecast trends and outcomes. Their support ensures accurate model building and interpretation, making complex predictive analysis accessible and manageable.
Needs help with similar assignment?
We are available 24x7 to deliver the best services and assignment ready within 3-4 hours? Order a custom-written, plagiarism-free paper