SAP Tutorial|2024
SAP Tutorial offers a comprehensive guide to mastering SAP systems, making it easier for users to navigate and utilize its powerful business tools. This resource is designed to simplify complex processes, enhance productivity, and build expertise in SAP applications. SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing) is one of the most widely used enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems globally. Businesses across various industries leverage SAP to streamline processes, improve data management, and make informed decisions. This tutorial provides a comprehensive overview of SAP, its core modules, and how businesses can benefit from implementing SAP solutions. Whether you’re a student, professional, or business owner, this guide will help you understand SAP and how to get started.
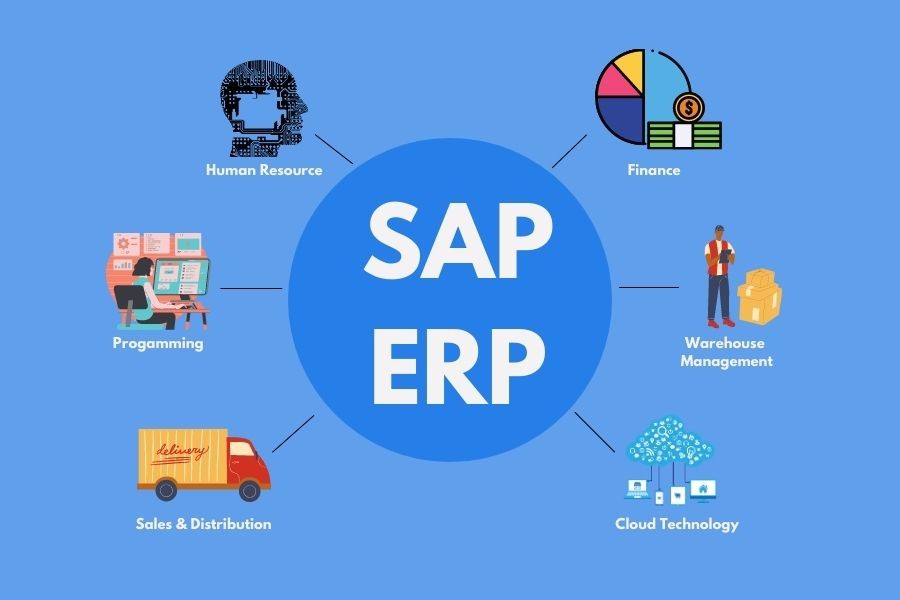 What is SAP?
What is SAP?
SAP is a German multinational software company founded in 1972. Its ERP solutions help organizations manage business operations and customer relations effectively. SAP software integrates all critical business functions, including finance, human resources, supply chain, and customer service, into a unified system.
The primary advantage of SAP is its ability to centralize data management, enabling organizations to eliminate redundancies, enhance productivity, and achieve better visibility across their operations.
Why Learn SAP?
- High Demand in the Job Market: SAP skills are in high demand, with many organizations seeking SAP consultants, analysts, and developers.
- Improved Career Prospects: Learning SAP can lead to lucrative career opportunities in various industries.
- Streamlined Business Processes: Professionals can optimize their organizations’ operations using SAP tools and solutions.
- Versatile Application: SAP is used in multiple domains, including finance, supply chain, manufacturing, and IT.
Key Features of SAP
- Modular Architecture: SAP is structured into modules that cater to specific business functions.
- Real-time Data Processing: SAP systems process data in real-time, ensuring timely decision-making.
- Scalability: SAP solutions can scale with the growth of an organization.
- Integration: Seamlessly integrates with other software and platforms.
- Customization: SAP systems can be tailored to meet unique business requirements.
SAP Modules Overview
SAP is divided into several modules, categorized into functional and technical areas:
Functional Modules
- SAP FICO (Financial Accounting and Controlling):
- Manages financial transactions, reporting, and accounts.
- Key Submodules: General Ledger (GL), Accounts Payable (AP), Accounts Receivable (AR), and Cost Center Accounting.
- SAP MM (Materials Management):
- Manages procurement and inventory processes.
- Key Features: Purchase Order Management, Inventory Management, and Vendor Evaluation.
- SAP SD (Sales and Distribution):
- Handles order management, pricing, and distribution.
- Key Features: Sales Orders, Shipping, and Billing.
- SAP HR (Human Resources):
- Manages employee data, payroll, and recruitment processes.
- Key Features: Time Management, Payroll, and Employee Self-Service.
- SAP PP (Production Planning):
- Focuses on production workflows and planning.
- Key Features: Material Requirement Planning (MRP) and Capacity Planning.
Technical Modules
- SAP ABAP (Advanced Business Application Programming):
- SAP’s programming language for developing applications.
- SAP BASIS:
- Provides technical support for SAP systems, including system installation and maintenance.
- SAP HANA (High-Performance Analytic Appliance):
- In-memory database platform for real-time analytics and data processing.
- SAP Security:
- Ensures data protection and user authentication.
Getting Started with SAP
Step 1: Understand Business Processes
Before diving into SAP, familiarize yourself with the business processes in your industry. Understanding workflows and requirements will help you grasp SAP modules better.
Step 2: Choose a Module
Select an SAP module that aligns with your career goals or organizational needs. For instance:
- Finance professionals can start with SAP FICO.
- HR professionals can explore SAP HR.
Step 3: Enroll in SAP Training
Join SAP training programs to gain hands-on experience. Online platforms like Coursera, LinkedIn Learning, and SAP’s official training portal offer excellent resources.
Step 4: Practice in a Sandbox Environment
Experiment with SAP systems in a sandbox or demo environment to understand the functionality and workflows.
Step 5: Get Certified
SAP certifications validate your expertise and make you stand out in the job market. Certifications are available for various modules and roles, such as SAP Consultant or Developer.
Benefits of SAP for Businesses
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automates repetitive tasks and streamlines processes.
- Improved Data Accuracy: Reduces manual errors through centralized data entry.
- Real-time Insights: Provides up-to-date information for informed decision-making.
- Compliance: Ensures regulatory compliance through built-in tools.
- Scalability: Grows with the organization’s needs.
Common Challenges and Solutions in SAP Implementation
Challenge 1: High Costs
Solution: Plan budgets carefully and explore cloud-based SAP solutions for cost-effectiveness.
Challenge 2: Complex Integration
Solution: Work with experienced SAP consultants to ensure smooth integration with existing systems.
Challenge 3: Resistance to Change
Solution: Provide comprehensive training and communicate the benefits to stakeholders.
Best Practices for SAP Users
- Regular Training: Keep up with updates and new features.
- Data Backup: Regularly back up data to prevent loss.
- User Access Control: Implement strict access controls to secure sensitive information.
- Monitor Performance: Use SAP tools to track system performance and address issues proactively.
- Leverage Analytics: Utilize SAP’s analytics capabilities to gain insights and drive growth.
Top Industries Using SAP
- Manufacturing: Manages supply chain, production, and logistics.
- Healthcare: Enhances patient care and hospital management.
- Retail: Optimizes inventory and customer service.
- Finance: Streamlines accounting and compliance.
- Telecommunications: Improves network and customer management.
Future of SAP
The future of SAP lies in integrating cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT). SAP is also heavily investing in cloud-based solutions to provide businesses with scalable and cost-effective tools. The SAP S/4HANA Cloud is one such example, enabling real-time analytics and improved decision-making.
Conclusion
SAP is a powerful tool for businesses looking to enhance their operations and achieve greater efficiency. By understanding its modules and functionalities, professionals can unlock career opportunities, and businesses can optimize processes. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to deepen your expertise, SAP offers vast resources to help you succeed. Start your SAP journey today and harness its potential for your career or business growth.
Needs help with similar assignment?
We are available 24x7 to deliver the best services and assignment ready within 3-4 hours? Order a custom-written, plagiarism-free paper




