How to Write a Strong Hypothesis|2025
/in General Articles /by BesttutorLearn how to write a strong hypothesis for your research. Discover tips to craft clear, testable statements that guide your study and support meaningful data analysis.
The formulation of a hypothesis is a critical first step in conducting research, whether in the fields of science, social sciences, or business. It serves as a prediction or an educated guess that the researcher seeks to test through experimentation or analysis. A well-crafted hypothesis is the backbone of a study, guiding the research process and helping the researcher to focus on specific objectives. This paper will explore the significance of a strong hypothesis, how to write one with the help of SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences), and how researchers can test it using data analysis techniques.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is a Hypothesis?
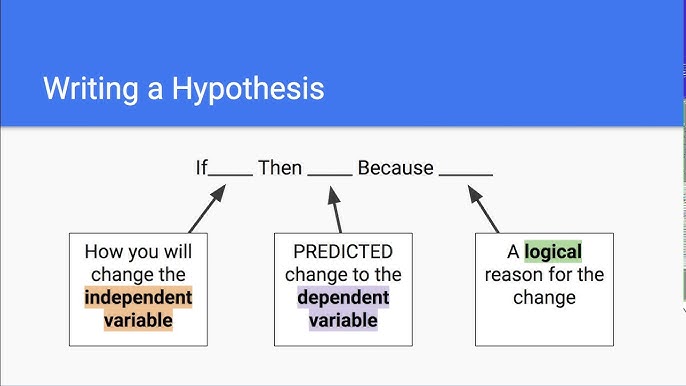
A hypothesis is a clear, testable statement that predicts the outcome of a study. It is formulated based on prior knowledge, observations, or theoretical concepts. The purpose of a hypothesis is to establish a relationship between variables, and it provides the foundation for designing research and interpreting data. Researchers use hypotheses to answer specific research questions and solve problems.
Key Elements of a Strong Hypothesis
Before diving into the process of writing a hypothesis with SPSS assistance, it’s important to understand the key elements that constitute a strong hypothesis:
- Testability: A hypothesis should be testable, meaning it can be supported or refuted through experimentation or data analysis.
- Clarity: The statement must be clear and concise.
- Specificity: It should focus on a particular relationship between variables.
- Predictive Nature: It should make a prediction about the outcome.
- Relevance: The hypothesis must be relevant to the research question.
Types of Hypotheses
Researchers typically formulate two types of hypotheses:
- Null Hypothesis (H₀): This hypothesis assumes no significant relationship or difference between variables. The null hypothesis is what researchers attempt to reject or disprove in their study.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H₁ or Ha): This hypothesis suggests that there is a significant relationship or difference between variables. The researcher aims to provide evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
How to Write a Hypothesis in Research
Writing a hypothesis involves several steps, which are outlined below:
- Identify the Research Problem: The first step in formulating a hypothesis is to clearly define the research question. What do you want to study or investigate?
- Conduct a Literature Review: Review existing literature related to your research problem to identify gaps in knowledge and to understand existing theories and findings. This will help you formulate a testable hypothesis.
- Define Your Variables: Identify the variables you plan to study. The independent variable is what you manipulate, and the dependent variable is what you measure.
- State the Hypothesis: Based on your research question, write a clear and concise hypothesis. If you believe there is a relationship between two variables, your hypothesis should specify the direction of this relationship (e.g., positive, negative, or no relationship).
- Make it Testable: Ensure that your hypothesis is testable through data analysis, observation, or experimentation.
- Refine the Hypothesis: After conducting initial testing or analysis, you may need to refine your hypothesis for clarity or to ensure that it fits the data.
Example of Hypothesis in Research Proposal PDF
An example of a research hypothesis in a proposal could be:
“There is a positive relationship between students’ study hours and their academic performance in university courses.”
This hypothesis is specific, testable, and focuses on the relationship between two variables: study hours (independent variable) and academic performance (dependent variable). Researchers could use statistical tools, including SPSS, to test the hypothesis.
Hypothesis Examples
Example 1: Simple Hypothesis
“Increasing the number of hours spent studying improves exam scores.”
This is a straightforward hypothesis that suggests a direct cause-and-effect relationship between study time (independent variable) and exam performance (dependent variable).
Example 2: Complex Hypothesis
“Higher levels of stress decrease the academic performance of college students, but the relationship is moderated by the amount of sleep they receive.”
In this complex hypothesis, stress, academic performance, and sleep all interact. Researchers would need advanced statistical methods to test such a hypothesis.
Example 3: Directional Hypothesis
“Women who exercise regularly have lower blood pressure compared to women who do not exercise regularly.”
This hypothesis specifies the direction of the relationship, predicting that regular exercise leads to lower blood pressure.
How to Write a Strong Hypothesis with SPSS Help
Once you have developed your hypothesis, SPSS can help you test it. The software is widely used for statistical analysis and hypothesis testing, offering a range of features that can assist researchers in analyzing their data.
Steps to Write and Test a Hypothesis Using SPSS
- Formulate Your Hypothesis: The first step is to clearly define your research question and hypothesis, just as outlined in earlier sections.
- Collect and Prepare Your Data: After you have a hypothesis in mind, the next step is to collect data relevant to your hypothesis. SPSS works with various data formats, such as Excel files, and allows you to import, organize, and clean your data.
- Choose the Right Statistical Test: Based on the nature of your hypothesis and data, select the appropriate statistical test. SPSS provides a wide range of tests, including:
- T-tests: Used to compare the means of two groups (e.g., comparing exam scores between male and female students).
- ANOVA (Analysis of Variance): Used to compare the means of more than two groups (e.g., comparing academic performance across multiple universities).
- Regression Analysis: Used to analyze relationships between dependent and independent variables (e.g., the relationship between study hours and exam performance).
- Chi-Square Tests: Used for categorical data to assess whether there is an association between two variables.
- Run the Statistical Test in SPSS: After selecting the appropriate test, input your data into SPSS, run the analysis, and examine the output. SPSS will generate results that include test statistics, p-values, and confidence intervals.
- Interpret the Results: Based on the p-value, determine whether you can reject the null hypothesis. A p-value less than 0.05 generally indicates that the results are statistically significant, meaning you can reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
- Draw Conclusions: After analyzing the data with SPSS, use the results to draw conclusions about your hypothesis. If your hypothesis is supported by the data, you can present your findings with confidence. If it is not supported, you may need to revise your hypothesis and conduct further research.
Example of Hypothesis Testing with SPSS
Suppose you want to test the hypothesis:
“There is a significant difference in the average test scores between students who study for 1-2 hours a day and students who study for 3-4 hours a day.”
- Data Preparation: You collect data on students’ study hours and their corresponding test scores.
- Statistical Test: You perform a t-test for independent samples in SPSS to compare the mean test scores between the two groups (1-2 hours vs. 3-4 hours).
- Results Interpretation: If the p-value is less than 0.05, you can conclude that there is a significant difference in test scores between the two groups, supporting your hypothesis.
How to Write a Hypothesis in Science
In scientific research, hypotheses are essential for guiding experiments. A scientific hypothesis must be testable, based on existing knowledge, and have clear variables. Here are steps for writing a hypothesis in science:
- Identify the Problem: Choose a scientific phenomenon that needs investigation.
- Do Background Research: Study existing literature to understand the current state of knowledge about the topic.
- Formulate the Hypothesis: Based on your research, make a prediction about the relationship between variables.
- Test the Hypothesis: Conduct experiments or gather data to test the hypothesis.
For example, if you are studying the effect of temperature on plant growth, you might hypothesize:
“Increasing the temperature will accelerate the growth of plants.”
This is a testable hypothesis that can be examined through experimentation.
How to Write a Hypothesis Example
Here is an example of how to write a hypothesis:
- Problem: Does regular exercise improve mental health?
- Hypothesis: “Regular physical exercise leads to a significant improvement in mental health in adults.”
This hypothesis is specific, testable, and suggests a cause-and-effect relationship between exercise (independent variable) and mental health (dependent variable).
Conclusion
Writing a strong hypothesis is a fundamental part of the research process. A well-formulated hypothesis allows the researcher to focus on specific variables, guide the design of experiments, and provide a framework for analyzing data. SPSS, a powerful statistical tool, helps researchers test their hypotheses and interpret data with precision. Whether you’re conducting scientific experiments, social science research, or business analysis, the process of writing a clear and testable hypothesis is the first step toward meaningful results.
Needs help with similar assignment?
We are available 24x7 to deliver the best services and assignment ready within 3-4 hours? Order a custom-written, plagiarism-free paper