What is a Concept Paper?|2025
/in General Articles /by BesttutorWhat is a Concept Paper?, and How Do You Write One Effectively? Learn the purpose, structure, and steps to create a clear and compelling concept paper for your project or research.
A concept paper is a brief document that outlines a project or idea and is used to gain approval or funding for that project. It serves as a tool to communicate the purpose, objectives, methodology, and significance of a proposal, often before a full proposal is developed. Concept papers are commonly used in academia, research institutions, and nonprofit organizations, but they can be valuable in various industries and sectors where new projects are being considered. This article will explore what a concept paper is, how to write one effectively, and provide examples and templates for better understanding.
What is a Concept Paper?
A concept paper is a concise, preliminary document that provides an overview of an idea, project, or research proposal. It aims to convey the essence of the project in a way that captures the attention of potential sponsors, stakeholders, or decision-makers. The purpose of a concept paper is to convince the reader that the proposed idea is valuable, feasible, and worthy of further development.
Although it is brief, a concept paper should be clear, structured, and persuasive. It may serve as the first step toward securing funding or approval for a project, but its goal is not to provide an exhaustive detail of the project itself. Rather, it offers just enough information to stimulate interest and encourage further discussion or evaluation.
The concept paper format may vary depending on the field and the specific requirements of the funding agency or institution, but there are certain elements that are typically included.
What Is a Concept Paper Format?
The structure of a concept paper is usually short and straightforward, typically ranging from 2 to 5 pages. While specific requirements may differ, the common components of a concept paper include:
- Title: A brief, descriptive title that gives an overview of the topic or focus of the proposal.
- Introduction or Background: A brief introduction to the topic, explaining the context and the problem the proposed project intends to address.
- Objectives: Clear, specific objectives that define what the project aims to accomplish. The objectives should be measurable and achievable within the scope of the project.
- Project Description or Methodology: A section outlining how the project will be carried out, including the methods, approach, and timeline. It may also describe the resources or strategies that will be used.
- Significance: A justification for why the project is important and how it will contribute to the field, solve a problem, or address a need. This section may highlight the potential impact or outcomes of the project.
- Expected Outcomes: A description of the outcomes that are anticipated from the project, which could include deliverables, results, or changes in the field.
- Budget Overview (optional): Some concept papers may include a brief budget outline, especially if the paper is being used to apply for funding.
- Conclusion: A final summary reiterating the importance of the project and how it will address the identified problem.
How to Write a Concept Paper
Writing an effective concept paper requires a clear understanding of the purpose of the document and the needs of the target audience. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to write a concept paper that effectively communicates your idea.
Identify the Purpose of Your Concept Paper
The first step in writing a concept paper is to understand why you are writing it. Are you seeking approval from a decision-maker? Are you applying for funding for a project? Your concept paper should be tailored to meet the expectations of the intended audience.
If you’re writing a concept paper to secure funding, for example, you will need to focus on demonstrating the potential impact of the project and how it aligns with the priorities or goals of the funding body. If you’re seeking approval for an idea, you’ll need to convince your readers of the feasibility and relevance of the project.
Research the Topic Thoroughly
Before writing, ensure that you fully understand the project or idea you’re proposing. This may involve conducting preliminary research, reviewing relevant literature, or gathering data to support the significance and feasibility of your proposal.
Clearly Define the Problem or Need
In the introduction of your concept paper, clearly articulate the problem or need that the project will address. This section should explain why the project is important and how it will benefit the target audience or field. Use data, statistics, or other supporting evidence to illustrate the severity of the issue and its relevance.
Establish Clear and Measurable Objectives
The objectives of your project should be well-defined and measurable. These objectives should answer the question: “What will this project achieve?” Be specific about what you aim to accomplish, and ensure that your objectives are realistic within the timeframe and resources available.
Describe the Project Methodology
In the project description section, explain how the project will be carried out. Outline the methods or approach you will use to achieve the stated objectives. This section may include details about the research design, project activities, or steps in the implementation process.
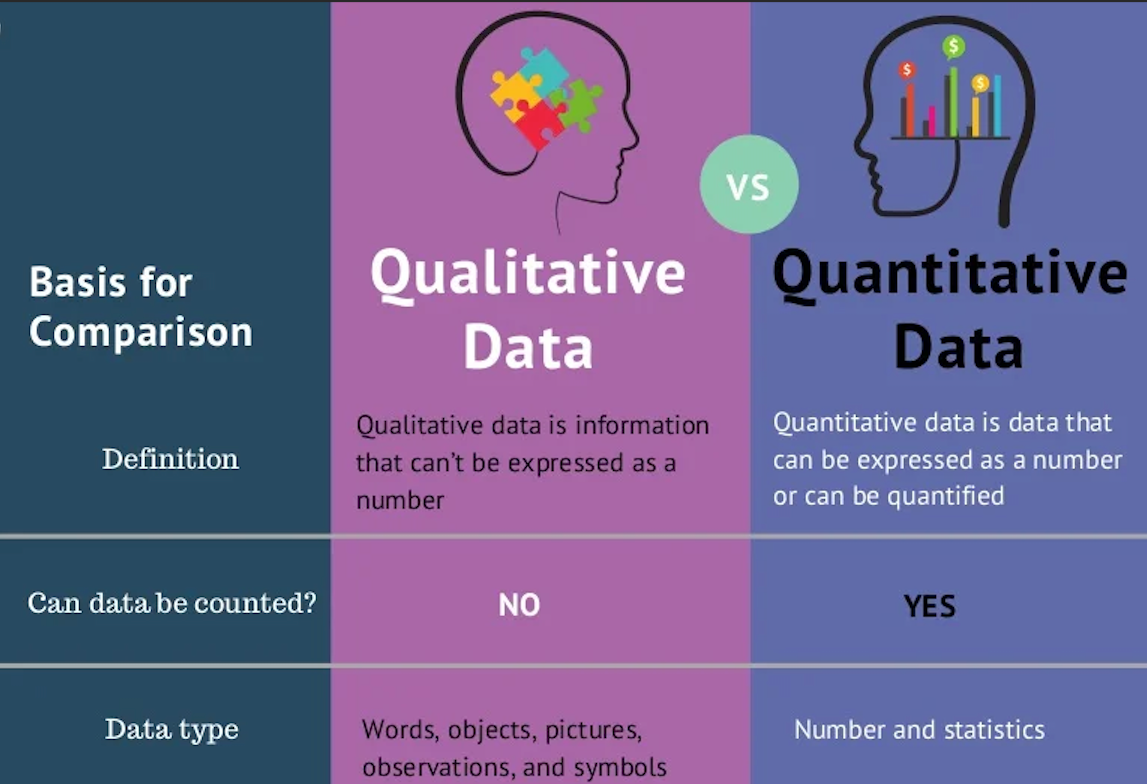
If your concept paper is about a research project, explain the research methodology (qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods), the data collection techniques, and any tools or instruments that will be used. If the project is more operational or service-oriented, describe the strategies and actions that will be employed.
Highlight the Significance of the Project
One of the most important sections of the concept paper is the justification or significance. Explain why the project matters and how it will make an impact. For example, if you’re proposing a research study, describe how it will contribute to existing knowledge in the field. If you’re proposing a community service project, explain how it will address a critical need or improve the lives of the target population.
Outline Expected Outcomes
Describe the expected outcomes of the project, including deliverables or measurable results. The outcomes should be directly linked to the objectives of the project. By doing so, you help the reader understand the tangible results that can be expected and how these outcomes will be assessed.
Include an Optional Budget Overview
If applicable, provide a brief outline of the project’s budget. This section doesn’t need to be as detailed as a full proposal but should give a rough estimate of the resources required for the project. This could include personnel costs, materials, equipment, or other expenses.
Conclude the Concept Paper
In the conclusion, summarize the key points of the concept paper and reinforce the importance of the project. Restate the problem, the objectives, and the potential impact of the project. The conclusion should leave the reader with a strong impression of the project’s value.
What Is a Concept Paper Example?
To better understand how to write a concept paper, it can be helpful to review a concept paper example. Below is an example of a simple concept paper based on a community health initiative:
Title: “Improving Access to Healthcare in Rural Communities”
Introduction: Access to healthcare remains a significant issue in many rural communities, where residents often face barriers such as long distances to medical facilities, lack of transportation, and limited healthcare providers. This concept paper proposes a community-based initiative aimed at improving healthcare access for residents of rural areas by establishing mobile healthcare units.
Objectives:
- To provide basic healthcare services to underserved rural communities.
- To reduce the number of emergency medical visits by offering preventive care.
- To increase health education in rural areas, focusing on preventative health practices.
Project Description: The project will involve the deployment of mobile healthcare units equipped with medical professionals, diagnostic tools, and health education materials. These units will visit rural communities on a rotating schedule, providing residents with primary care services, vaccinations, screenings, and health education sessions.
Significance: This initiative will significantly reduce the barriers to healthcare faced by rural communities and will improve the overall health outcomes of the population by focusing on preventative care.
Expected Outcomes:
- 75% of rural residents within the target areas will have access to basic healthcare services.
- A 50% reduction in preventable health-related emergencies within the first year.
- Increased awareness of preventive health practices in rural communities.
Budget Overview:
- Personnel (doctors, nurses, and support staff): $150,000
- Mobile unit equipment: $50,000
- Operational costs: $20,000
Conclusion: This project will provide much-needed healthcare services to underserved rural populations, improving health outcomes and reducing preventable health emergencies. It aligns with the goal of improving healthcare equity and accessibility in rural areas.
Concept Paper Sample PDF and Examples
If you’re looking for more examples or sample PDFs of concept papers, there are several online resources where you can find templates and samples. These samples can help guide you in crafting your own concept paper. Be sure to adapt any sample or template to fit the specific requirements of the funding body or institution you’re targeting.
Here are 10 examples of concept paper topics across various fields:
- Mobile Health Clinics in Low-Income Urban Areas
- Renewable Energy Solutions for Rural Communities
- Digital Literacy Training for Senior Citizens
- Reducing Plastic Waste in Urban Centers
- Creating a Support System for Homeless Veterans
- Developing an Online Platform for Mental Health Support
- Enhancing Child Nutrition in Developing Countries
- Promoting Women’s Empowerment Through Entrepreneurship
- Reducing Traffic Congestion with Public Transportation Improvements
- Expanding Access to Higher Education for Underserved Youth
Conclusion
Writing a concept paper is an essential skill for anyone involved in project management, research, or proposal writing. It serves as the first step in obtaining approval, support, or funding for a new initiative. By following the format and structure outlined above, and using clear, concise language, you can effectively communicate your ideas and convince your audience of the importance and feasibility of your proposal. Whether you’re writing for a research project, community service initiative, or business plan, a well-crafted concept paper is the foundation for a successful endeavor.
Needs help with similar assignment?
We are available 24x7 to deliver the best services and assignment ready within 3-4 hours? Order a custom-written, plagiarism-free paper