How To Implement Factor Analysis In Your Research|2025
/in General Articles /by BesttutorLearn how to implement factor analysis in your research. Discover key steps, techniques, and tips for analyzing complex data and identifying underlying patterns.
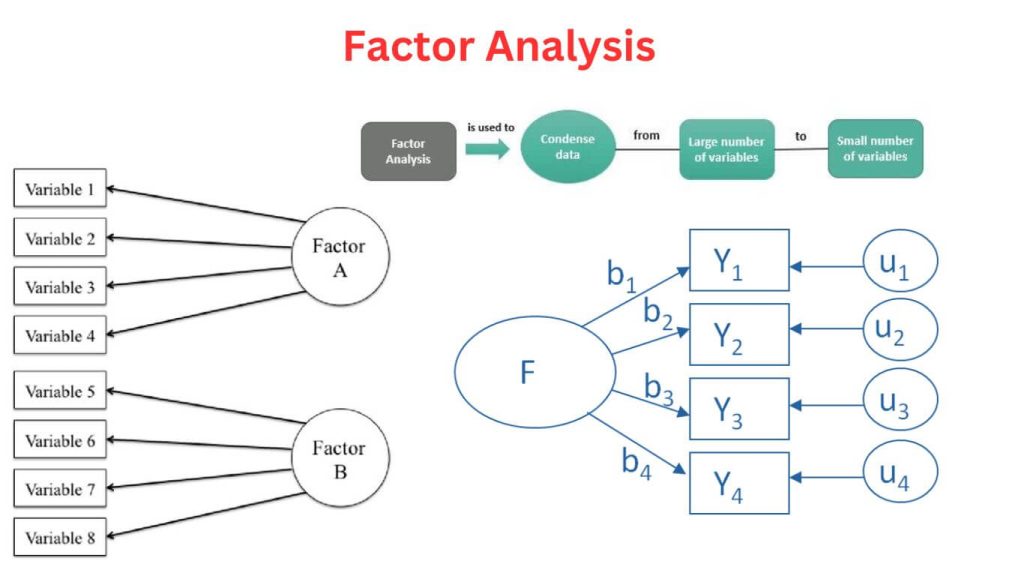
Factor analysis is a multivariate statistical technique used to identify the underlying relationships between observed variables. It helps researchers reduce data complexity by grouping variables into factors that are assumed to represent an underlying structure. Factor analysis is particularly useful when a researcher has a large number of variables and seeks to identify patterns or groupings within the data that would simplify further analysis.
This paper aims to guide researchers on how to implement factor analysis in their research, by discussing the following key topics:
- How to Implement Factor Analysis in Your Research Sample
- How to Implement Factor Analysis in Your Research Example
- Factor Analysis in Research Methodology PDF
- How to Do Factor Analysis in Research
- Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA)
- What Is Factor Analysis in Psychology
- Factor Analysis Example
Table of Contents
ToggleHow to Implement Factor Analysis in Your Research Sample
The implementation of factor analysis requires a structured approach to ensure that the technique is applied correctly and that the results are meaningful. Below are the steps to take when implementing factor analysis in your research sample:
Data Collection
To begin, ensure that you have a sufficient number of observations and variables. Factor analysis typically requires at least five participants per variable, though a larger sample size (e.g., 200 or more) is preferred for more reliable results.
Variables Selection
Factor analysis is most effective when used with variables that are continuous in nature. For instance, it works well with survey data where responses are measured on scales (e.g., Likert scale items). Ideally, these variables should be interrelated in some way. This technique helps in identifying patterns or latent structures within the data, and it is important that the variables chosen reflect commonalities.
Checking for Suitability of Data
Before proceeding, you must check the suitability of your data for factor analysis using tests such as:
- Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) Test: This test measures the sampling adequacy. Values closer to 1 indicate that factor analysis is suitable for the dataset, with values above 0.6 considered acceptable.
- Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity: This test examines whether the correlation matrix is an identity matrix, which would suggest that the data is not suitable for factor analysis. A significant result (p < 0.05) suggests that factor analysis can be performed.
Preliminary Data Screening
Data cleaning is essential to ensure that there are no missing values, outliers, or multicollinearity among the variables. Missing data can be handled using imputation methods or by excluding participants with incomplete responses. You should also check for any multicollinearity, as highly correlated variables can distort the results of factor analysis.
How to Implement Factor Analysis in Your Research Example
Let’s consider an example of a researcher investigating how different factors (such as attitudes toward work, personality traits, and job satisfaction) influence employee performance. The researcher collects survey responses on variables like motivation, job satisfaction, leadership styles, and work-life balance. Factor analysis can be used to group these variables into distinct factors that explain the underlying dimensions of employee performance.
Steps for Implementing Factor Analysis:
- Data Collection: The researcher collects responses from 500 employees across 10 variables that assess different aspects of employee performance and satisfaction.
- Test Data Suitability: The researcher checks the KMO value and Bartlett’s test. If results show that the data is suitable for factor analysis, they proceed.
- Choose Extraction Method: The researcher decides on the extraction method. Common techniques include Principal Component Analysis (PCA) or Principal Axis Factoring (PAF).
- Determine Number of Factors: The researcher examines the eigenvalues and scree plot to determine the number of factors to retain.
- Rotation: The researcher performs varimax rotation (an orthogonal rotation) to improve interpretability.
- Interpret Results: The researcher interprets the factor loadings to determine the meaning of each factor (e.g., one factor may represent leadership styles, while another represents job satisfaction).
By the end of this process, the researcher will have a set of factors that can explain the underlying patterns in employee performance, which will help in designing better interventions to improve employee productivity.
Factor Analysis in Research Methodology PDF
A Factor Analysis in Research Methodology PDF could serve as a comprehensive guide for researchers interested in understanding the technicalities of factor analysis. Such a document would typically include:
- Introduction to Factor Analysis: Explanation of the need for factor analysis in research and its historical development.
- Theoretical Framework: Overview of the theory behind factor analysis, including the concept of latent variables and the factor model.
- Methodology: Step-by-step instructions for conducting factor analysis, including data collection, data screening, factor extraction, rotation methods, and interpretation of results.
- Applications: Case studies and examples of how factor analysis has been used in various fields like psychology, social sciences, business, and health research.
- Interpretation of Results: Detailed explanation of how to interpret factor loadings, communalities, and other factor analysis outputs.
How to Do Factor Analysis in Research
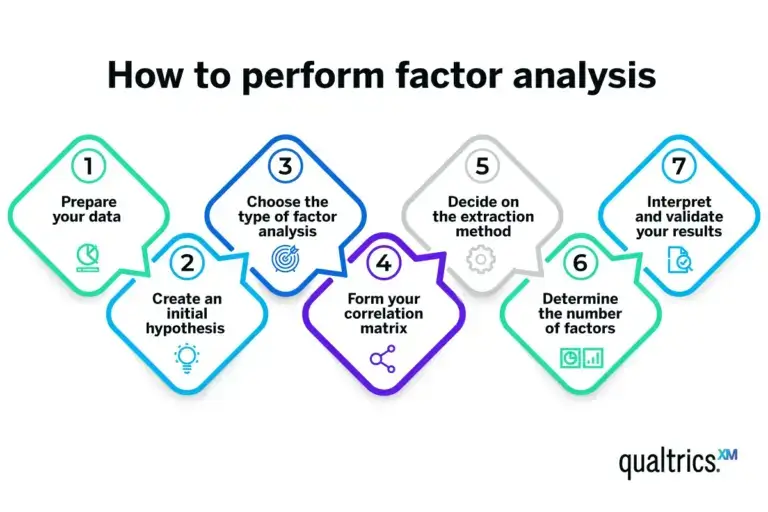
Implementing factor analysis in research follows a systematic process, which can be broken down as follows:
1. Select the Software: Factor analysis is commonly performed using statistical software like SPSS, R, or Stata. Each software has specific functions and tools for performing the analysis.
2. Data Input: Input your dataset into the software, ensuring that the variables are correctly labeled.
3. Run Factor Analysis:
- Choose Extraction Method: PCA is often used for data reduction, while other methods like PAF or Maximum Likelihood are used for identifying underlying latent variables.
- Rotation: Apply a rotation method, such as varimax (orthogonal) or oblimin (oblique), depending on whether you assume that the factors are correlated.
4. Review Output: After running the factor analysis, the software will provide outputs like eigenvalues, factor loadings, and communalities. Look at the eigenvalues to determine how many factors should be retained (typically, those with eigenvalues greater than 1).
5. Interpret Results: Analyze the factor loadings to identify which variables are strongly associated with each factor. A variable is considered strongly associated with a factor if its loading exceeds 0.4.
6. Refinement: Sometimes, the initial model might need refinement by adjusting the number of factors or removing poorly loading variables.
Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA)
Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) is used when researchers do not have a preconceived theory or structure about the factors. EFA helps in exploring the underlying structure of a large set of variables. It is typically used in the early stages of research when the goal is to uncover patterns and generate hypotheses.
Key Steps in EFA:
- Data Preparation: Ensure that the sample size is adequate, the data is continuous, and there are no significant missing values.
- Factor Extraction: Use techniques like PCA or PAF to extract factors.
- Rotation: Apply varimax or oblimin rotation to make the factors more interpretable.
- Factor Retention: Use criteria like the Kaiser criterion (eigenvalue > 1) or the scree plot to determine how many factors to retain.
- Interpretation: Review the factor loadings to understand which variables belong to which factors.
EFA is particularly useful when a researcher is unsure about the number of factors or the relationships between variables.
What Is Factor Analysis in Psychology?
In psychology, factor analysis is commonly used to identify the underlying psychological constructs or traits that explain observed behaviors. For example, factor analysis is frequently applied in personality research, where it helps in identifying factors like openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism (the Big Five personality traits). Factor analysis in psychology can be particularly useful for:
- Identifying latent constructs: For example, using factor analysis to identify factors like anxiety, depression, and stress based on responses to psychological assessments.
- Scale development: When developing new psychological tests or questionnaires, researchers often use factor analysis to validate the scales and ensure they measure distinct psychological traits.
- Theory testing: Factor analysis helps in testing theories about how different psychological constructs are related to one another.
Factor Analysis Example
Let’s consider an example from the field of psychology:
A researcher is studying mental health and collects data on 10 variables, including levels of anxiety, depression, self-esteem, and social isolation. The goal is to identify whether these variables can be grouped into distinct factors related to psychological well-being.
By applying factor analysis, the researcher might find that:
- Factor 1: Anxiety and Depression
- Factor 2: Self-esteem and Social Isolation
This indicates that anxiety and depression are strongly related to each other, and self-esteem and social isolation are related. The researcher can then use this information to refine mental health interventions by focusing on these two factors.
Conclusion
Implementing factor analysis in your research can help simplify complex data, uncover hidden patterns, and reduce dimensionality. Whether you are working with psychological data, social sciences, business surveys, or any other field, factor analysis is a powerful tool that helps in identifying the relationships between variables and guiding future research directions. By following the appropriate steps—from data collection to interpreting results—you can effectively apply factor analysis and gain valuable insights from your data.
Needs help with similar assignment?
We are available 24x7 to deliver the best services and assignment ready within 3-4 hours? Order a custom-written, plagiarism-free paper