Institutional Review Boards (IRBs): Their Role, Importance, and Effective Strategies for Researchers
/in General Articles /by BesttutorInstitutional Review Boards. Learn about the role, importance, and processes of IRBs in ensuring ethical standards and protecting participants in research studies.
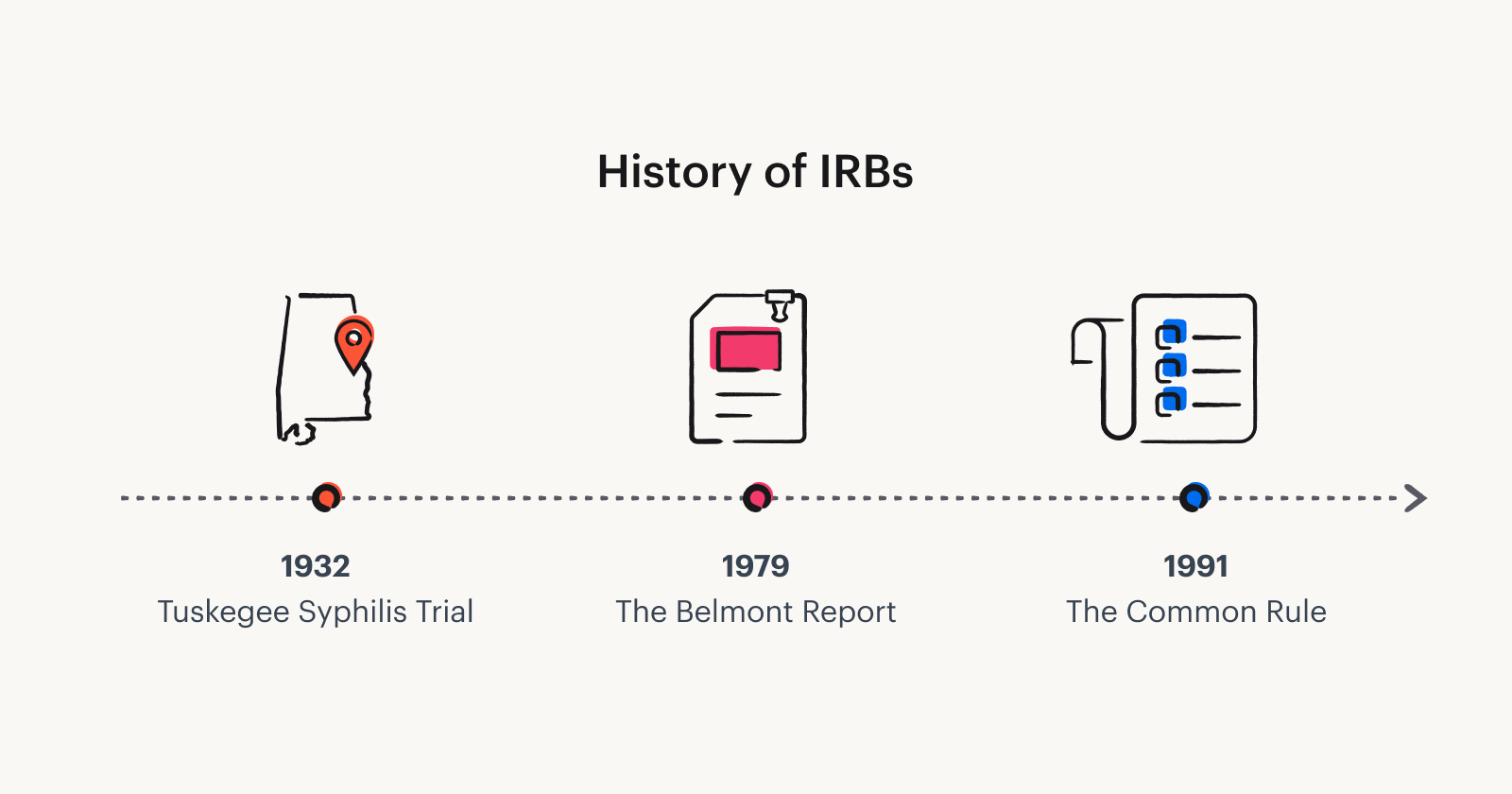
An Institutional Review Board (IRB) is a group of individuals responsible for reviewing, approving, and monitoring research involving human subjects. The goal of an IRB is to ensure that ethical standards are met in the design and conduct of research, protecting the rights and welfare of participants. The concept of institutional review emerged in response to historical unethical research practices, such as the infamous Tuskegee Syphilis Study and the Nazi medical experiments. Today, IRBs are essential components of research institutions worldwide, overseeing a wide range of academic and clinical studies.
This paper will explore the role of Institutional Review Boards, providing examples of their functions, a discussion on how to get IRB approval, and a look into the relevance of IRBs in different fields like psychology. Additionally, strategies for investigators to successfully navigate the IRB process will be presented.
Table of Contents
ToggleInstitutional Review Board: Definition and Purpose
An Institutional Review Board is a committee tasked with overseeing research projects that involve human participants. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the primary purpose of the IRB is to ensure that the rights and welfare of human research participants are protected. The IRB evaluates research proposals based on criteria such as risk, benefit, and the informed consent process. By reviewing these factors, the IRB ensures that any potential harm to participants is minimized, and that the research is conducted in a manner consistent with ethical guidelines.
While the exact structure and procedures may vary between institutions, an IRB typically includes a diverse group of experts, including individuals with scientific and non-scientific backgrounds, ethicists, and community representatives. This diversity helps ensure that the review process is comprehensive and balanced.
Institutional Review Board Example: How They Function
An example of how an IRB operates can be found in academic research settings, where IRBs review research proposals from students, faculty, and staff. For instance, consider a psychology department at a university that is conducting research on the effects of social media use on adolescent mental health. The researchers would submit their research proposal to the university’s IRB, including detailed information on their methodology, potential risks to participants, and how they will obtain informed consent.
The IRB would assess the proposal to determine whether the research meets ethical standards. In this case, the IRB might review aspects such as the confidentiality of participant data, how minors will be protected in the study, and whether there is adequate debriefing after the research. If the IRB finds the proposal to be ethically sound, they would grant approval to proceed with the research.
On the other hand, if the IRB identifies significant ethical concerns—such as a lack of informed consent or exposure to unnecessary harm—the researchers would be asked to revise the proposal to address these issues before approval is granted.
Institutional Review Board Website and Resources
Many institutions have dedicated websites for their IRB services, where researchers can find resources and instructions for submitting research proposals for review. These websites typically provide important information about the submission process, deadlines, required documentation, and guidelines for preparing a research proposal that complies with ethical standards.
For instance, the IRB website at a major research university might include forms for submitting a research protocol, guidelines for writing consent forms, and frequently asked questions (FAQs) to help researchers navigate the process. Researchers may also find information about the types of review—such as expedited, full board, or exempt review—based on the nature and risk level of the research. Websites often provide contact information for IRB coordinators who can assist with any questions or concerns.
A typical Institutional Review Board website may also offer resources for investigators about the ethical principles underlying the review process, such as the Belmont Report, which outlines respect for persons, beneficence, and justice as key ethical principles in research involving human subjects.
How to Get IRB Approval
Obtaining IRB approval is a critical step in any research study that involves human subjects. The process of getting IRB approval typically involves several key steps:
- Initial Preparation: Researchers should familiarize themselves with the ethical guidelines and IRB requirements of their institution. They should ensure that their research plan addresses all ethical considerations, such as informed consent, participant confidentiality, and minimizing potential risks.
- Submit a Research Proposal: The next step is to submit a detailed research proposal to the IRB. This proposal should include information about the research design, recruitment process, informed consent process, risks, benefits, and how the data will be collected and stored.
- IRB Review Process: Once the proposal is submitted, the IRB will review it to ensure that the study complies with ethical guidelines and federal regulations. The level of review will depend on the nature of the research and the level of risk involved. For example, low-risk studies may be eligible for expedited review, while higher-risk studies may require full board review.
- Approval or Revisions: If the IRB finds the proposal to be ethical, they will grant approval. If the IRB identifies concerns, they may ask the researcher to revise the proposal or address specific issues before approval is granted.
- Ongoing Monitoring: After approval, the IRB may require periodic progress reports from the researchers to ensure that the study continues to adhere to ethical standards. Additionally, any major changes to the research methodology or participant recruitment process must be submitted for further review.
The IRB process helps safeguard the welfare of participants and ensures that researchers uphold ethical standards throughout the study.
Institutional Review Psychology: The Role of IRBs in Psychological Research
Psychology is a field that frequently involves human participants, making the role of the IRB especially critical. In psychological research, IRBs review studies that examine a wide variety of issues, including cognition, behavior, and mental health. Given the sensitive nature of psychological research, such as studies involving vulnerable populations or the potential for emotional distress, IRBs play an essential role in ensuring that participants are treated ethically.
For example, a psychology researcher studying the effects of therapy on anxiety might propose a study that requires participants to share personal experiences and undergo a series of therapy sessions. The IRB would carefully review the study to ensure that participants are fully informed about the nature of the therapy, any potential risks involved, and their right to withdraw at any time without penalty.
Additionally, IRBs ensure that researchers in psychology are adhering to confidentiality standards and that data are handled securely. This is particularly important in psychological research where sensitive personal information might be gathered.
List of Institutional Review Boards: National and International Variations
There is a wide variety of Institutional Review Boards around the world, each with specific guidelines and procedures. A few notable examples include:
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) IRB: This federal agency is responsible for overseeing research involving human subjects in the United States, particularly in the fields of health and medicine.
- Office for Human Research Protections (OHRP): This office provides guidance on the ethical conduct of research in the U.S. and supports IRBs across the country in ensuring compliance with federal regulations.
- The NHS Health Research Authority (UK): In the United Kingdom, the Health Research Authority oversees ethical review processes for health-related research, providing a framework for IRBs in the UK.
- Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC): In Australia, this council provides guidance and funding for health-related research, including ethical review by Institutional Review Boards.
IRB Research: Investigators’ Strategies for Success
For researchers seeking IRB approval, understanding the review process is crucial for success. Below are some strategies that can help investigators navigate the IRB process effectively:
- Prepare Thoroughly: A well-prepared proposal that clearly outlines the research design, recruitment procedures, and ethical considerations can help facilitate the approval process. Researchers should take care to ensure that informed consent forms are clear, comprehensive, and accessible to participants.
- Understand the Review Levels: Not all research requires the same level of review. Researchers should be familiar with the types of reviews available, such as expedited or full board review, and select the appropriate category based on the nature and risks of the research.
- Address Ethical Concerns Upfront: Anticipating potential ethical concerns and addressing them in the proposal can expedite the approval process. For example, addressing potential risks to participants and explaining how those risks will be mitigated can show that the research design prioritizes participant safety.
- Engage with the IRB Early: Many researchers benefit from engaging with the IRB early in the planning stages of their research. By discussing their study with IRB members before formally submitting a proposal, researchers can identify potential issues and address them proactively.
- Stay Transparent and Flexible: If the IRB requests revisions or additional information, researchers should be responsive and transparent. Modifying a proposal to meet the IRB’s concerns is often necessary for approval.
Conclusion
Institutional Review Boards play a vital role in ensuring that research involving human participants is conducted ethically and responsibly. By reviewing proposals, monitoring ongoing research, and safeguarding participants’ rights, IRBs help maintain the integrity of scientific research. Understanding the IRB process—how to get IRB approval, the role of the board in psychology, and successful strategies for researchers—can streamline the approval process and ultimately enhance the ethical standards of research. Researchers who prioritize ethical conduct and collaborate effectively with IRBs will contribute to the advancement of knowledge while ensuring the protection and welfare of participants.
Needs help with similar assignment?
We are available 24x7 to deliver the best services and assignment ready within 3-4 hours? Order a custom-written, plagiarism-free paper