Integrating Data Analysis Skills into Undergraduate Curriculum|2025
/in General Articles /by BesttutorDiscover the benefits of integrating data analysis skills into undergraduate curriculum. Learn how incorporating data-driven learning enhances critical thinking, research abilities, and academic success.
In the modern world, data plays a crucial role in almost every industry and domain. From healthcare to education, businesses, and government policy, data has become a driving force behind decision-making processes. With the vast amount of information generated daily, the ability to interpret, analyze, and make sense of this data is essential. In education, the importance of data analysis cannot be overstated, as it empowers students to engage with real-world challenges, make informed decisions, and enhance their critical thinking skills. Consequently, integrating data analysis skills into the undergraduate curriculum is essential to prepare students for the demands of the contemporary workforce.
This paper explores the significance of data analysis in education, its practical applications, the topics covered in data analytics courses, and how universities can integrate these skills into their curricula. Additionally, it provides insights into where students can practice data analysis and the benefits of acquiring these skills for future career prospects.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is the Purpose of Data Analysis in Education?
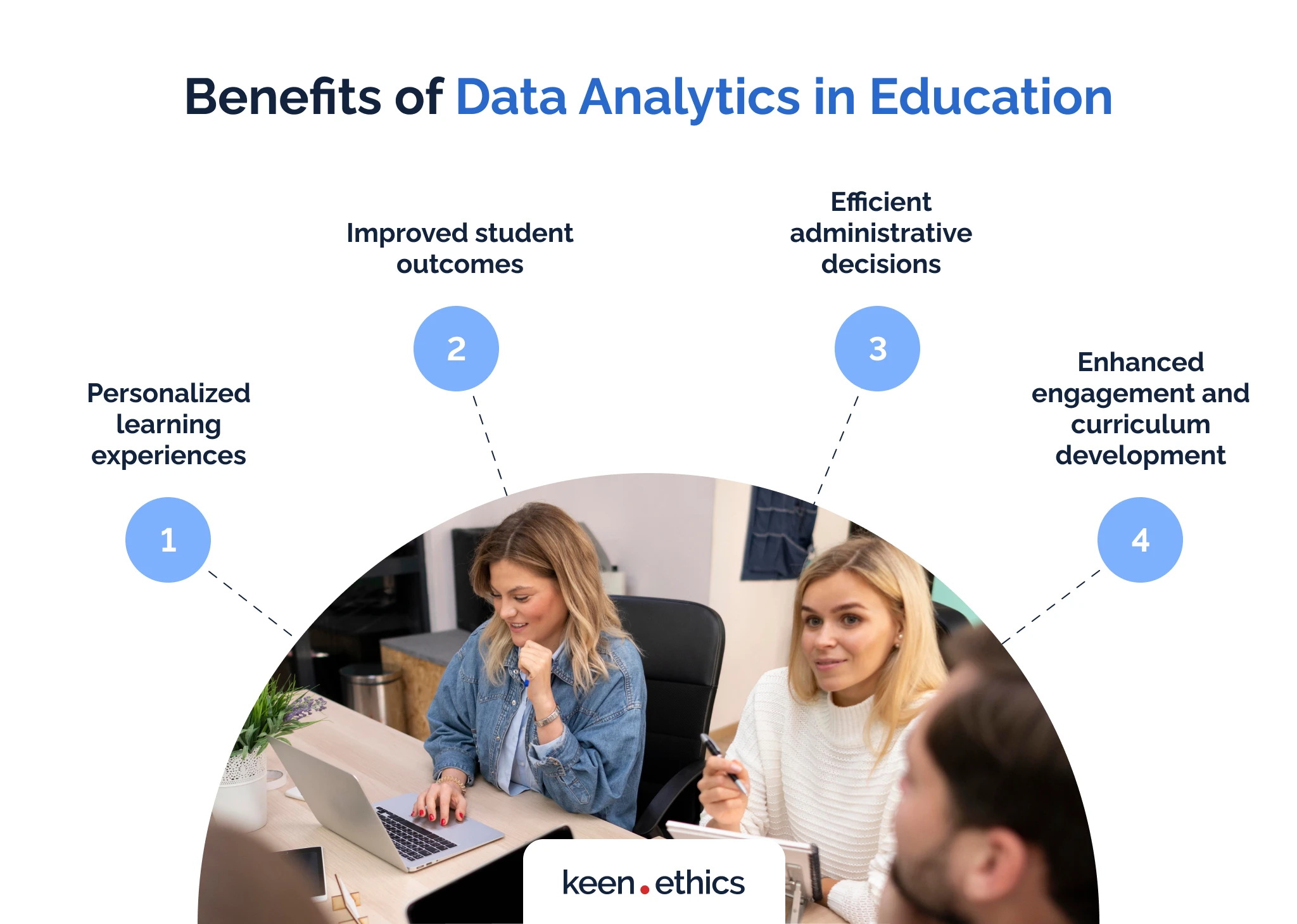
Data analysis is the process of systematically examining data to extract meaningful insights, identify trends, and make informed decisions. In education, the primary purpose of data analysis is to enhance the learning experience, improve instructional strategies, and inform policy decisions. By integrating data analysis into the educational process, educators can:
- Improve Student Outcomes: Data analysis helps educators identify patterns in student performance, track progress over time, and tailor interventions to meet individual learning needs. By using data-driven insights, teachers can personalize learning experiences, offer targeted support, and ultimately improve student outcomes.
- Evaluate Teaching Effectiveness: Through data analysis, educators can assess the effectiveness of their teaching methods, instructional materials, and course design. This process allows for continuous improvement and ensures that instructional practices align with student needs and learning objectives.
- Inform Policy and Curriculum Development: Data analysis in education extends beyond the classroom. By analyzing trends and patterns in educational systems, policymakers can make informed decisions about curriculum design, resource allocation, and educational reforms. Data-driven policies have the potential to drive systemic change and improve education on a larger scale.
- Encourage Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving: Integrating data analysis into the curriculum helps students develop critical thinking skills. Students learn how to approach complex problems, identify relevant data, and make evidence-based conclusions. These skills are valuable not only in academic settings but also in real-world scenarios.
- Enhance Research Capabilities: For students pursuing careers in research, data analysis is an essential skill. It enables students to design studies, collect data, analyze results, and draw conclusions. Research in fields such as psychology, sociology, economics, and education itself often relies on data analysis to validate hypotheses and contribute to knowledge.
In short, the purpose of data analysis in education is to improve student learning, inform decision-making processes, and prepare students for the demands of a data-driven world. As data becomes increasingly important across various sectors, students must be equipped with the skills necessary to analyze and interpret data effectively.
What Are the Main Topics in Data Analytics?
Data analytics is a broad field encompassing various topics, tools, and techniques used to extract insights from data. In an undergraduate curriculum, the following are some of the main topics typically covered in data analytics courses:
- Data Collection and Cleaning: The first step in any data analysis process is gathering relevant data. Students learn how to collect data from various sources, such as surveys, experiments, or databases. Data cleaning involves identifying and correcting errors, handling missing values, and transforming raw data into a usable format for analysis.
- Descriptive Statistics: Descriptive statistics involve summarizing and visualizing data to uncover trends, patterns, and distributions. Students are introduced to key concepts such as mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and variance. Graphical representations such as histograms, box plots, and scatter plots are used to display data and identify relationships.
- Inferential Statistics: Inferential statistics involves making predictions or generalizations about a population based on a sample of data. Students learn techniques such as hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and regression analysis to draw conclusions and test hypotheses.
- Data Visualization: Data visualization is the art of presenting data in a visual format to make it easier to understand and interpret. Students learn to create charts, graphs, and dashboards that convey insights effectively. Data visualization tools such as Tableau, Power BI, and Excel are commonly used in this process.
- Machine Learning and Predictive Analytics: As data becomes more complex, students are introduced to machine learning techniques that enable computers to learn from data and make predictions. Students learn about supervised and unsupervised learning, decision trees, clustering, and regression models. Predictive analytics uses historical data to forecast future trends and outcomes.
- Big Data and Cloud Computing: With the explosion of data in recent years, the concept of big data has become increasingly relevant. Students learn about the challenges and opportunities presented by large-scale datasets, as well as tools and platforms for storing and processing big data. Cloud computing services such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure play a critical role in managing and analyzing big data.
- Data Ethics and Privacy: Data analysis involves ethical considerations regarding privacy, consent, and data security. Students are introduced to the ethical implications of data collection and analysis, including issues related to bias, discrimination, and the responsible use of data.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The ultimate goal of data analysis is to support decision-making. Students learn how to use data to make informed decisions in various contexts, such as business, healthcare, public policy, and education. This topic emphasizes the importance of evidence-based decision-making and the limitations of data analysis.
These topics are essential for providing students with a comprehensive understanding of data analytics. As the field continues to evolve, students must also stay abreast of new developments and tools to remain competitive in the job market.
What is Covered in a Data Analytics Course?
A typical data analytics course covers a wide range of concepts, tools, and techniques to provide students with the skills needed to analyze and interpret data. While the specific content of a course may vary depending on the institution and the course’s focus, the following are some key areas commonly addressed:
- Introduction to Data Analysis: Students are introduced to the fundamentals of data analysis, including its purpose, process, and significance. They also learn about the types of data (e.g., qualitative vs. quantitative) and common data sources.
- Statistical Techniques: A significant portion of a data analytics course is devoted to teaching students statistical methods, including descriptive and inferential statistics. Students learn how to apply statistical tests, such as t-tests and chi-square tests, to analyze data and draw conclusions.
- Data Manipulation and Analysis with Software Tools: Students are trained to use software tools such as Excel, R, Python, and SQL to manipulate and analyze data. They learn how to clean, transform, and analyze data using these tools.
- Data Visualization: A major component of data analytics courses is data visualization. Students learn how to create visual representations of data using various tools, such as Tableau or Matplotlib in Python, to present their findings in a clear and compelling way.
- Advanced Analytical Techniques: For more advanced courses, students may delve into machine learning algorithms, data mining, predictive modeling, and big data analytics. These techniques are used to analyze large and complex datasets and make predictions based on historical data.
- Project-Based Learning: Many data analytics courses incorporate project-based learning, where students work on real-world datasets to apply their analytical skills to solve practical problems. These projects help students gain hands-on experience and develop a portfolio of work to showcase to potential employers.
- Data Ethics and Privacy: Ethical considerations in data analysis are addressed, focusing on the responsible use of data, the prevention of bias, and the protection of privacy.
Through a combination of lectures, hands-on activities, and projects, students gain the knowledge and skills necessary to perform data analysis tasks effectively. By the end of the course, students should be able to apply data analytics techniques to solve problems, make data-driven decisions, and communicate their findings clearly.
Where Can I Practice My Data Analysis Skills?
There are numerous ways to practice and refine data analysis skills outside the classroom. These platforms provide students with the opportunity to work on real-world datasets, collaborate with others, and gain practical experience in data analysis.
- Kaggle: Kaggle is a popular platform for data science and machine learning competitions. It offers a wide variety of datasets and challenges, allowing students to apply their data analysis skills in a competitive environment. Kaggle also has a strong community where users can collaborate and share insights.
- DataCamp: DataCamp is an online learning platform that offers interactive courses in data analysis, machine learning, and programming. The platform provides hands-on exercises, projects, and quizzes to help students practice their skills.
- UCI Machine Learning Repository: The UCI Machine Learning Repository is a collection of datasets for machine learning and data analysis. Students can use these datasets to practice their skills in data cleaning, analysis, and modeling.
- GitHub: GitHub is a platform for version control and collaborative coding. Many data analysis projects are shared on GitHub, providing students with the opportunity to contribute to open-source projects and showcase their work.
- Online Competitions and Hackathons: Many organizations host online data analysis competitions and hackathons. These events provide students with an opportunity to work on real-world problems, collaborate with others, and gain exposure to industry challenges.
- Internships and Research Projects: Participating in internships or research projects provides students with valuable hands-on experience in data analysis. These opportunities allow students to work with real datasets, apply their skills in a professional setting, and gain insights into the practical applications of data analysis.
By engaging with these platforms and opportunities, students can gain practical experience, build a portfolio, and develop the confidence needed to apply data analysis skills in their future careers.
Conclusion
As the world becomes increasingly data-driven, the need for individuals with strong data analysis skills is more significant than ever. Integrating data analysis into the undergraduate curriculum is essential for preparing students for the challenges and opportunities of the modern workforce. By understanding the purpose of data analysis in education, the topics covered in data analytics courses, and where to practice these skills, students can develop the expertise necessary to succeed in a variety of fields. Ultimately, data analysis is a critical skill that empowers individuals to make informed decisions, solve complex problems, and contribute to positive change in society.
Needs help with similar assignment?
We are available 24x7 to deliver the best services and assignment ready within 3-4 hours? Order a custom-written, plagiarism-free paper