Qualitative vs Quantitative Data: Understanding the Distinctions|2025
/in General Articles /by BesttutorDiscover the key differences between Qualitative vs Quantitative Data, their unique characteristics, and how to effectively use each type for research and analysis.
Data serves as the backbone of research, offering insights and evidence that drive informed decisions and conclusions. In the world of research, data is often categorized into two main types: qualitative and quantitative. Each type of data serves different purposes, utilizes distinct methodologies, and offers different advantages. Understanding the distinctions between these two types of data is crucial for selecting the right approach for any research project. This paper explores the key differences, provides examples, and discusses the importance of both qualitative and quantitative data in research.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Qualitative Data?
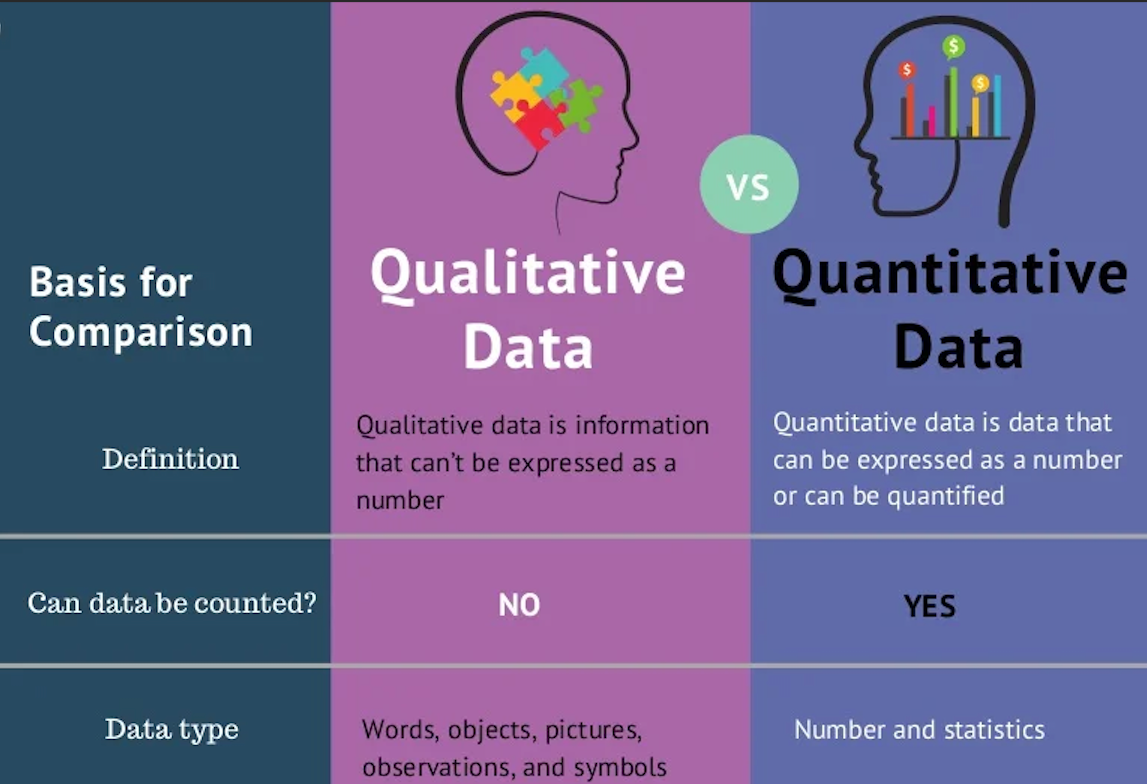
Qualitative data is non-numeric and focuses on the qualities or characteristics of a subject rather than quantifiable measurements. It is often descriptive and provides a deeper understanding of underlying phenomena. This type of data is typically used in exploratory research to identify patterns, insights, or concepts that require further investigation.
Qualitative data is commonly used in fields such as psychology, sociology, anthropology, and education, where understanding human behavior, experiences, and perceptions is essential. It is collected through open-ended questions, interviews, observations, and case studies. Qualitative data can include text, images, video, or audio recordings, making it rich and detailed but also subjective.
Examples of Qualitative Data:
- Interviews: Responses from an open-ended interview about a person’s life experiences.
- Observations: Descriptive notes on how a group of people behaves during a meeting.
- Textual Data: The content of a group discussion or a social media post expressing opinions or emotions.
What is Quantitative Data?
Quantitative data, on the other hand, deals with numbers and measurable forms. It focuses on quantities and is used to quantify variables, allowing researchers to conduct statistical analysis. This data type is used to test hypotheses, validate theories, and identify relationships between variables. Quantitative data is objective, structured, and can be analyzed using mathematical or statistical methods.
Quantitative research methods include surveys, experiments, and observational studies that involve measurable variables. It is commonly used in fields like economics, biology, and market research, where the goal is to produce measurable and generalizable results.
Examples of Quantitative Data:
- Survey Data: A questionnaire where respondents rate their satisfaction on a scale from 1 to 10.
- Sales Figures: The number of units sold by a company in a given period.
- Temperature Readings: The recorded temperature at different times during the day.
Key Differences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Data
The primary distinction between qualitative and quantitative data lies in the nature of the information they represent. These differences can be summarized in several key aspects:
Nature of Data:
-
- Qualitative data is descriptive and focuses on qualities, characteristics, and experiences. It is often subjective and can vary based on individual perspectives.
- Quantitative data is numerical and deals with quantities and measurements. It is objective and provides concrete figures that can be analyzed statistically.
Research Approach:
-
- Qualitative research is often exploratory and seeks to understand underlying meanings, experiences, or phenomena. It emphasizes in-depth analysis of a smaller sample size.
- Quantitative research is confirmatory and aims to quantify relationships, patterns, or variables. It typically involves larger sample sizes and focuses on statistical analysis.
Data Collection Methods:
-
- Qualitative data is collected through interviews, focus groups, observations, and content analysis.
- Quantitative data is collected using structured tools such as surveys, questionnaires, and experiments that produce numerical results.
Analysis Techniques:
-
- Qualitative analysis involves coding and categorizing data to identify themes, patterns, and meanings. It is often more interpretive and flexible.
- Quantitative analysis uses statistical methods such as regression analysis, t-tests, and chi-square tests to determine relationships, averages, and trends.
Outcome:
-
- Qualitative data produces rich, detailed narratives and insights that offer a deeper understanding of a subject.
- Quantitative data produces measurable, generalizable results that can be applied to larger populations.
Examples of Qualitative and Quantitative Data:
- A qualitative example could be analyzing a focus group discussion on consumer preferences, where researchers gather opinions, feelings, and insights about a product.
- A quantitative example could involve analyzing the number of units sold by a company in a year, which is a measurable quantity that can be used for forecasting or performance evaluation.
Difference Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research
The difference between qualitative and quantitative research lies in their respective goals, methods, and approaches to data collection and analysis.
Qualitative Research:
-
- Goal: To explore, understand, and interpret phenomena, typically from a subjective standpoint.
- Methodology: Uses unstructured or semi-structured methods such as interviews, focus groups, and participant observations. Data analysis is more flexible, relying on interpretation and theme identification.
- Outcome: Generates in-depth insights into people’s experiences, motivations, or behaviors, but results are not easily generalized.
Quantitative Research:
-
- Goal: To quantify variables, test hypotheses, and establish patterns or relationships that can be generalized.
- Methodology: Uses structured instruments such as surveys, tests, and experiments to collect numerical data. Data analysis involves statistical techniques and hypothesis testing.
- Outcome: Provides generalizable results, often with a high degree of reliability, but may lack the depth of understanding found in qualitative research.
The Difference Between Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis
In terms of analysis, qualitative and quantitative methods diverge significantly.
Qualitative Analysis:
-
- Qualitative analysis is more interpretive and often involves a thematic or content analysis approach. Researchers look for patterns and themes in the data, organize the findings into categories, and interpret the meaning behind these findings. Qualitative analysis is flexible and allows for the exploration of nuanced details.
- For example, in a study of consumer behavior, a qualitative analysis might examine the reasons behind customers’ purchasing decisions, including emotional or social factors.
Quantitative Analysis:
-
- Quantitative analysis involves using statistical tools to test hypotheses or examine relationships between variables. It aims to produce objective, quantifiable results. Researchers apply numerical data to calculate measures like averages, frequencies, and correlations. The analysis often involves the use of software like SPSS, R, or Excel.
- For example, a quantitative analysis might examine the correlation between advertising spending and sales revenue over time, using regression analysis to quantify the strength of the relationship.
Similarities Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Despite their differences, qualitative and quantitative research share several similarities:
- Data Collection: Both types of research involve systematic data collection processes to ensure reliability and validity.
- Rigorous Methods: Both qualitative and quantitative research require researchers to apply rigorous methods to gather and analyze data.
- Purpose: Both approaches aim to advance knowledge and understanding, though they do so in different ways.
- Complementary: Qualitative and quantitative research can be used together in mixed-methods studies to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a research problem. For example, qualitative insights can inform the design of a quantitative survey, and quantitative findings can validate qualitative results.
Conclusion
In conclusion, qualitative and quantitative data represent two distinct but equally important approaches to research. Qualitative data offers depth, context, and richness, often revealing underlying meanings and human experiences. Quantitative data, on the other hand, provides measurable, objective, and generalizable results that are crucial for hypothesis testing and statistical analysis.
Understanding the distinctions between qualitative and quantitative data is essential for selecting the appropriate research methodology. Researchers must carefully consider the nature of the research question, the type of data required, and the desired outcomes to determine the most effective approach. Furthermore, the integration of both qualitative and quantitative methods can provide a well-rounded perspective, offering both detailed insights and broader generalizability. By mastering both approaches, researchers can enhance the scope and impact of their work in various disciplines.
Needs help with similar assignment?
We are available 24x7 to deliver the best services and assignment ready within 3-4 hours? Order a custom-written, plagiarism-free paper