Noteworthy Steps to Write a Systematic Literature Review|2025
Discover noteworthy steps to write a systematic literature review. Learn how to organize, evaluate, and present research effectively for academic and professional success.
Systematic literature reviews (SLRs) are critical for synthesizing existing knowledge in a structured and replicable manner. They help researchers identify gaps in the literature, establish evidence for decision-making, and provide a foundation for further study. This paper outlines the noteworthy steps to write a systematic literature review and offers examples, methodological guidance, and resources such as systematic literature review sample PDFs to assist researchers in various fields, including medical studies. By following these steps, you can create a robust SLR that adheres to academic and professional standards.
Understanding Systematic Literature Reviews
A systematic literature review is a type of research methodology that collects, evaluates, and synthesizes all available evidence on a specific research question. Unlike traditional narrative reviews, SLRs use a transparent and rigorous process to minimize bias and ensure reproducibility. For instance, the “7 steps of systematic review” framework provides a comprehensive roadmap for conducting SLRs systematically.
Importance of Systematic Literature Reviews
SLRs play a pivotal role in various disciplines, particularly in medicine, where evidence-based practices are paramount. For example, a systematic literature review PDF focusing on the efficacy of a new drug offers a clear and concise synthesis of all relevant clinical trials. Researchers can then rely on such reviews to inform policy decisions, guideline development, or further investigation.
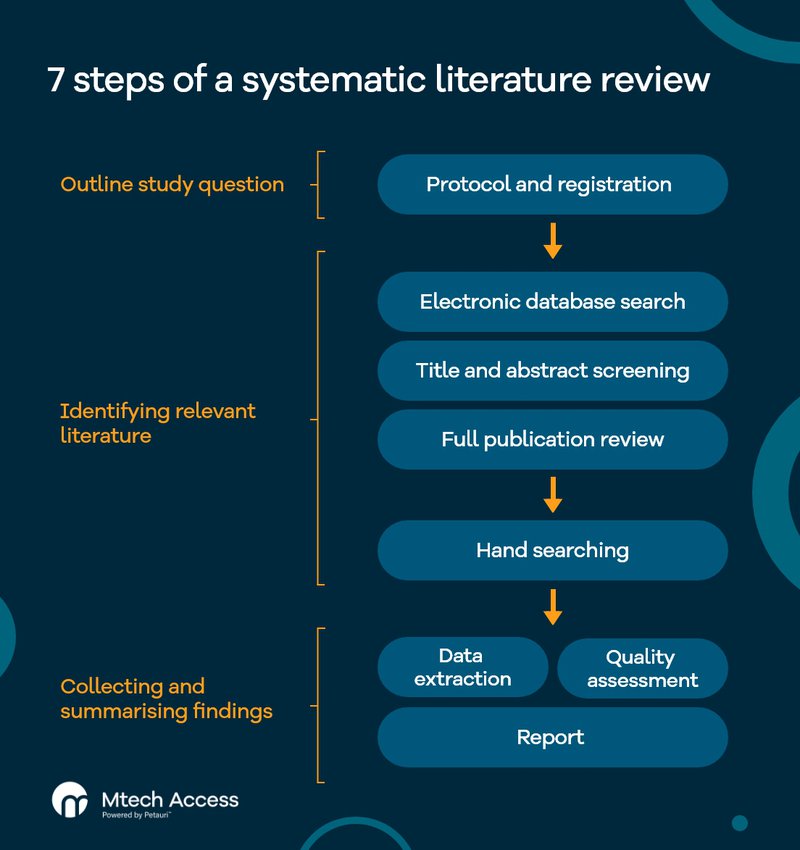
Noteworthy Steps to Write a Systematic Literature Review
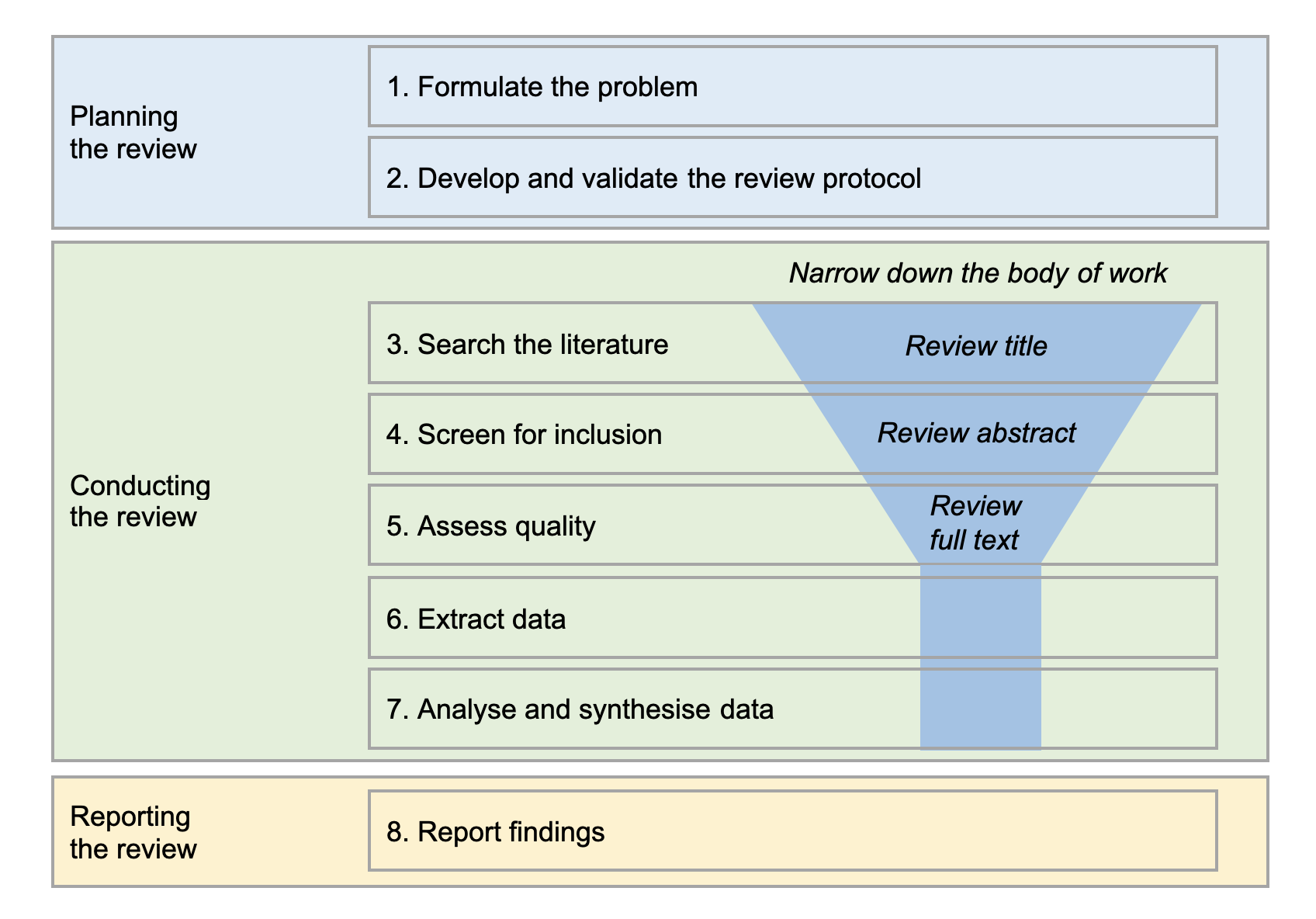
Below are the detailed steps involved in writing an SLR. These steps align with established frameworks like the “6 steps in conducting a systematic review” and “7 steps of systematic review.”
Define the Research Question
The foundation of an SLR lies in a clear, focused research question. Use the PICOS (Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Study design) framework to formulate your question, particularly in medical research. For instance, a research question could be:
“What is the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy compared to pharmacotherapy in treating anxiety disorders?”
Develop a Protocol
A systematic review protocol outlines the methods and processes you’ll follow, ensuring transparency and reducing bias. The protocol should include:
- Research objectives
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Search strategy
- Data extraction and synthesis methods
Consider registering your protocol on platforms like PROSPERO to enhance credibility.
Conduct a Comprehensive Literature Search
Perform a thorough search across multiple databases such as PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science. Use a combination of keywords, Boolean operators, and controlled vocabulary to ensure comprehensive coverage. For example:
- Keywords: “systematic literature review example,” “systematic literature review sample PDF,” “6 steps in conducting a systematic review.”
- Boolean Search: (“Systematic literature review” OR “SLR”) AND (“methodology” OR “example”)
Screen and Select Studies
Use predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria to screen studies. Tools like PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) flow diagrams can help document the selection process. Ensure:
- Titles and abstracts are screened for relevance.
- Full-text reviews confirm eligibility.
Assess the Quality of Included Studies
Evaluate the quality and risk of bias in the selected studies using established tools like the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool or Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. This step is crucial for ensuring the reliability of your findings.
Extract Data
Develop a standardized data extraction form to collect key information, such as:
- Study design
- Sample characteristics
- Interventions
- Outcomes
Synthesize and Analyze Data
Data synthesis can be qualitative or quantitative (meta-analysis). Choose an appropriate approach based on the nature of your studies. Use software like RevMan or NVivo for data analysis. Ensure your synthesis highlights patterns, discrepancies, and gaps in the literature.
Report Results
Present your findings in a structured manner using established guidelines like PRISMA. Include sections such as:
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Methods
- Results
- Discussion
- Conclusion
Interpret and Discuss Findings
Discuss the implications of your findings, limitations of your review, and recommendations for future research. For example, a systematic literature review PDF on a new treatment might emphasize the need for larger, high-quality randomized trials.
Publish and Disseminate
Submit your SLR to relevant journals or share it via academic platforms. Publishing enhances the visibility and impact of your research.
Systematic Literature Review Methodology: An Example
To illustrate the process, consider a systematic literature review example focusing on “The Effectiveness of Telemedicine in Chronic Disease Management.”
Step 1: Define Research Question
“How effective is telemedicine in improving health outcomes for patients with chronic diseases?”
Step 2: Develop Protocol
The protocol specifies databases (e.g., PubMed, Embase), inclusion criteria (e.g., randomized controlled trials, studies published in English), and analysis methods.
Step 3: Literature Search
Search terms: “telemedicine,” “chronic disease management,” “systematic review.”
Step 4: Screen Studies
Use PRISMA to document the selection of 50 studies from an initial pool of 500.
Step 5: Assess Quality
Apply the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool to assess study reliability.
Step 6: Extract Data
Key outcomes: patient satisfaction, hospitalization rates, and cost-effectiveness.
Step 7: Synthesize Data
A meta-analysis reveals telemedicine’s significant impact on reducing hospitalizations by 20%.
Step 8: Report Results
The findings are presented in a systematic literature review PDF, structured per PRISMA guidelines.
Resources for Writing Systematic Literature Reviews
Systematic Literature Review Sample PDFs
- Access examples from reputable journals to understand formatting and reporting standards.
Software Tools
- EndNote: For managing references.
- Covidence: For screening studies.
- RevMan: For conducting meta-analyses.
Guidelines and Frameworks
- PRISMA for reporting.
- Cochrane Handbook for methodology.
Challenges in Writing Systematic Literature Reviews
While SLRs are invaluable, they pose challenges such as:
- Time-intensive processes.
- Difficulty in accessing full-text articles.
- Managing large volumes of data.
Overcoming these challenges requires meticulous planning, access to robust resources, and collaboration.
Conclusion
Writing a systematic literature review involves a rigorous and transparent process to synthesize existing research. By following the “6 steps in conducting a systematic review” or the “7 steps of systematic review,” researchers can ensure their work is comprehensive, reliable, and impactful. Leveraging resources such as systematic literature review sample PDFs and methodological guidelines enhances the quality and credibility of the review. Whether you are exploring how to write a systematic literature review as a guide for medical research or other fields, adhering to these steps will lead to success in producing a high-quality SLR.
Needs help with similar assignment?
We are available 24x7 to deliver the best services and assignment ready within 3-4 hours? Order a custom-written, plagiarism-free paper