The Four Types of Qualitative Research and Methods for Conducting Them|2025
/in General Articles /by BesttutorExplore the four types of qualitative research & methods for conducting them. Learn about case studies, ethnography, phenomenology, and grounded theory to enhance your research skills.
Qualitative research is an umbrella term that covers various methods of inquiry aimed at understanding human behavior, experiences, interactions, and social phenomena. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data, qualitative research delves into the complexities of the subject matter, exploring meanings, perceptions, and context. The objective is to explore the underlying reasons, motivations, and the “why” behind human actions. This paper will examine the four main types of qualitative research methods and provide insights into conducting each of them. Additionally, we will explore the 6 and 7 types of qualitative research, offer examples, and explore the relevant aspects of qualitative research design.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Four Types of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research can be classified into various types, each serving specific purposes and using different techniques. Below, we will examine four major types of qualitative research, offering a framework for conducting each.
1. Case Study Research
A case study is an in-depth investigation into a single person, group, event, or situation, which is analyzed within its real-life context. Case studies are useful for gaining insights into complex phenomena and understanding the nuances of a specific instance. They are often employed in psychology, sociology, education, business, and law.
Methods for Conducting Case Study Research:
- Selection of Cases: The first step in conducting case study research is selecting appropriate cases. This could involve choosing individuals, groups, or organizations that illustrate the research problem.
- Data Collection: Case studies often use multiple sources of data, such as interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts.
- Data Analysis: Data analysis involves identifying patterns and themes from the collected information and organizing them into categories for deeper insight.
- Triangulation: Researchers may use triangulation to validate the data by comparing findings from different sources, ensuring the research’s credibility.
Example:
A researcher studying the impact of community-based education programs on marginalized youth might focus on a specific community program. They would collect data through interviews with participants, educators, and community leaders, as well as observing program sessions.
2. Ethnography
Ethnography is the study of cultures and communities through direct observation. This method involves immersing oneself in the community or group being studied to understand their social practices, behaviors, and beliefs. Ethnographers often participate in the daily life of their subjects, which gives them an insider’s perspective.
Methods for Conducting Ethnography:
- Fieldwork: Ethnographic research typically requires researchers to spend extended periods within the community being studied, observing and sometimes participating in activities.
- Participant Observation: Ethnographers take part in daily activities, often blending in with the community to observe behaviors and interactions from within.
- Interviews: Informal and formal interviews are conducted with community members to gain further insight into their perspectives.
- Analysis: Data analysis is usually qualitative, involving the identification of patterns and themes within the observations and interviews.
Example:
An ethnographer researching a remote indigenous tribe may live with the community for several months, learning their language, rituals, and social practices to understand their worldview and cultural identity.
3. Phenomenological Research
Phenomenology focuses on understanding human experiences from the perspective of those who lived through them. Researchers using this method aim to describe the essence of experiences and how individuals perceive their reality. This approach is commonly used in psychology and social sciences.
Methods for Conducting Phenomenological Research:
- Bracketing: Researchers must bracket, or set aside, their own experiences and biases to focus solely on the participants’ perspectives.
- In-depth Interviews: Open-ended, deep interviews are conducted to allow participants to share their experiences and thoughts freely.
- Data Analysis: The collected data is analyzed to identify themes and patterns that represent the essence of the experiences described by the participants.
- Member Checking: After data analysis, researchers may return to the participants to validate the findings.
Example:
A researcher exploring the experiences of cancer survivors may conduct interviews with patients, seeking to understand how they perceive the emotional and psychological challenges of their diagnosis and treatment.
4. Grounded Theory
Grounded theory is a systematic methodology that aims to generate theories based on data collected from participants. The goal is to develop a theory that is grounded in the data rather than testing existing theories. This method is commonly used in social sciences, particularly in sociology and psychology.
Methods for Conducting Grounded Theory Research:
- Data Collection: Researchers collect data through various means such as interviews, observations, and surveys.
- Open Coding: The initial step in analysis involves breaking down the data into small, meaningful segments called “codes.”
- Constant Comparative Method: Data is constantly compared and contrasted to refine categories and build a theory.
- Memo Writing: Researchers write memos throughout the research process to capture their thoughts and insights, which helps in developing the theory.
- Theory Development: The final stage involves the development of a theory that explains the patterns found in the data.
Example:
A grounded theory study might investigate how employees cope with workplace stress. Researchers would conduct interviews and observations, develop initial codes related to coping mechanisms, and refine these codes to eventually build a theory about stress management in the workplace.
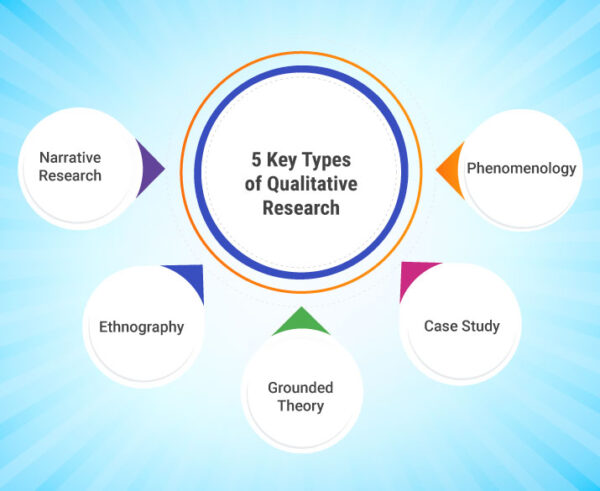
The 6 Types of Qualitative Research
Beyond the four main types discussed above, researchers often encounter additional approaches within qualitative research. These include:
- Narrative Research: Narrative research focuses on the stories people tell about their lives. Researchers collect narratives through interviews and focus groups, analyzing the structure and content of these personal accounts to gain deeper insights into human experiences.
- Action Research: Action research involves the active participation of researchers and subjects in solving a problem or improving a situation. It is often used in educational settings and community-based research.
- Content Analysis: Content analysis involves systematically analyzing written, spoken, or visual materials to identify patterns, themes, or biases within the content.
- Participatory Research: Participatory research is a collaborative process where the subjects of research are actively involved in the research process.
- Discourse Analysis: This method focuses on the ways in which language is used in social contexts. Discourse analysis examines texts, conversations, and interactions to explore how language shapes perceptions and social realities.
- Visual Research: Visual research focuses on the use of visual materials such as photographs, videos, and artworks to understand cultural and social phenomena.
The 7 Types of Qualitative Research
In some frameworks, qualitative research is categorized into seven types, including the six mentioned above, with the addition of:
- Focus Group Research: Focus group research involves guided group discussions where participants share their opinions, experiences, and perceptions about a specific topic. The researcher moderates the discussion and analyzes the group’s interactions and feedback.
Qualitative Research Methods PDF
The qualitative research methods PDF can be a useful resource for gaining an understanding of how each of these research types is conducted. It often includes detailed guidelines, best practices, and sample templates for researchers. By referring to such documents, researchers can ensure they follow systematic procedures for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting qualitative data.
Types of Qualitative Research PDF
Similarly, types of qualitative research PDFs typically outline the various approaches and methodologies, providing a roadmap for researchers. These documents can assist in identifying the most suitable method based on the research objectives, whether it’s case study research, ethnography, or any other qualitative approach.
What Are the 7 Types of Qualitative Research?
As mentioned earlier, the seven types of qualitative research include case study, ethnography, phenomenology, grounded theory, narrative research, action research, and focus group research. Each type is designed to explore different aspects of human behavior and society, offering distinct advantages depending on the research questions.
Qualitative Research Examples
Qualitative research examples can be found across various fields of study. Here are a few examples:
- Health Care: Studying patient experiences during long-term illness through interviews to understand the emotional and psychological challenges.
- Education: Observing classroom behavior to understand the interaction between teachers and students and the impact of teaching methods on learning.
- Sociology: Analyzing social movements by conducting interviews with activists to understand their motivations and the challenges they face.
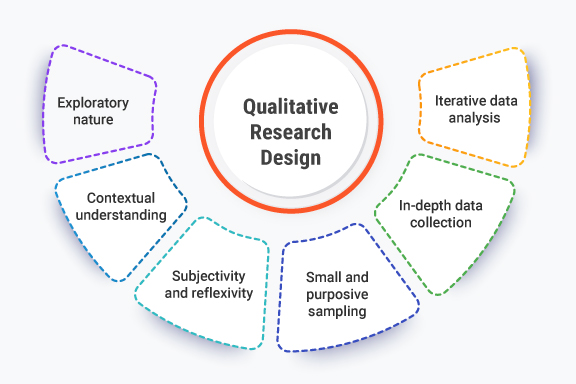
Qualitative Research Design
Qualitative research design refers to the plan and structure of a qualitative study. The design includes the research question, the selected method (e.g., ethnography or case study), data collection techniques (e.g., interviews or observations), and data analysis strategies. A well-structured qualitative research design is essential to ensure that the study remains focused and the findings are valid and reliable.
Key Elements of Qualitative Research Design:
- Research Questions: The design begins with formulating research questions that are open-ended and exploratory.
- Sampling: Researchers typically use purposive sampling to select participants who can provide rich insights into the research question.
- Data Collection: Data collection methods can include interviews, focus groups, observations, and document analysis.
- Data Analysis: Data is analyzed thematically, looking for recurring patterns, meanings, and insights.
- Ethical Considerations: Ethical issues such as informed consent and confidentiality must be addressed in qualitative research.
Conclusion
Qualitative research encompasses a range of methods that provide valuable insights into human experiences, behaviors, and social phenomena. The four main types—case study, ethnography, phenomenology, and grounded theory—offer distinct approaches for exploring complex issues. Researchers also use various supplementary methods like narrative research, action research, and focus groups to deepen their understanding. By using these qualitative research methods, researchers can uncover the underlying motivations, patterns, and cultural contexts that shape human life. Proper research design, ethical considerations, and thorough data analysis are essential for conducting high-quality qualitative research.
Needs help with similar assignment?
We are available 24x7 to deliver the best services and assignment ready within 3-4 hours? Order a custom-written, plagiarism-free paper