Understanding Statistical Significance in SPSS: A Beginner’s Guide|2025
Statistical significance is a fundamental concept in data analysis, particularly in research settings where it helps validate findings. For beginners using SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences), understanding statistical significance can seem overwhelming. This guide aims to demystify the concept and provide actionable steps for interpreting statistical significance in SPSS effectively. By the end, you will have a solid foundation to confidently analyze and present your data.
What is Statistical Significance?
Statistical significance indicates whether the results of an analysis are likely due to chance or if they represent genuine relationships in the data. In simpler terms, it tells you if your findings are reliable enough to make inferences about a larger population.
Key Terms:
- p-value: The probability that the observed results occurred by chance. A p-value less than 0.05 is typically considered statistically significant.
- Null Hypothesis (H0): A statement that assumes no effect or no difference exists in the data.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H1): A statement that assumes an effect or difference exists.
- Alpha Level (α): The threshold set by researchers (commonly 0.05) to determine statistical significance.
Importance of Statistical Significance in SPSS
1. Validation of Findings
Statistical significance ensures that your results are not due to random chance, lending credibility to your research.
2. Decision-Making
It provides a basis for accepting or rejecting hypotheses, aiding in data-driven decisions.
3. Reproducibility
Significant results are more likely to be reproducible, strengthening the reliability of research.
Steps to Understand Statistical Significance in SPSS
Step 1: Input and Prepare Your Data
- Open SPSS and load your dataset.
- Clean your data by addressing missing values and errors.
- Define variables appropriately (e.g., categorical or continuous).
Step 2: Choose the Right Test
The choice of statistical test depends on your research question and data type:
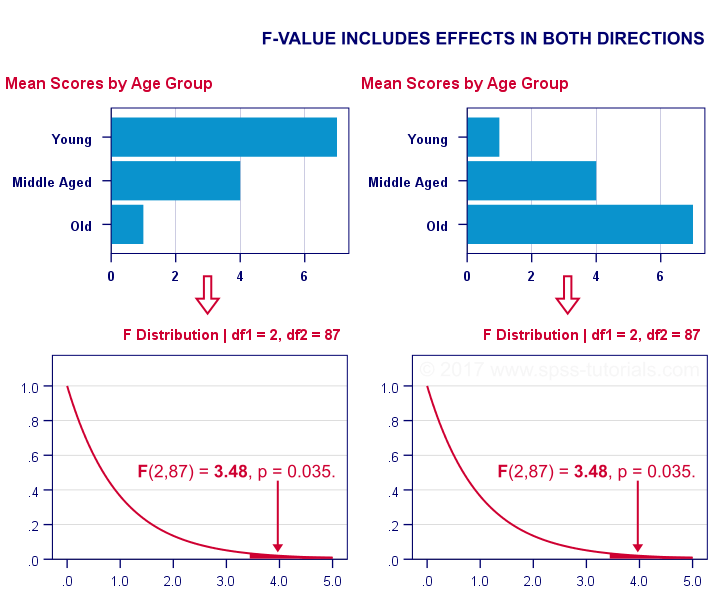
- t-tests: Compare means between two groups.
- ANOVA: Compare means across multiple groups.
- Chi-Square Test: Assess relationships between categorical variables.
- Correlation: Measure the strength of relationships between continuous variables.
- Regression: Analyze the impact of one or more predictors on an outcome.
Step 3: Run the Analysis
- Navigate to the appropriate menu in SPSS (e.g., Analyze > Compare Means > Independent-Samples T-Test).
- Select your dependent and independent variables.
- Specify test options and execute the analysis.
Step 4: Interpret the Outputs
- Look for the p-value in the output table.
- Compare the p-value to your alpha level (α = 0.05):
- If p < α, reject the null hypothesis.
- If p ≥ α, fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Step 5: Report Your Findings
- Clearly state whether the results were statistically significant.
- Include relevant metrics (e.g., mean differences, effect sizes) for context.
Examples of Statistical Significance in SPSS
1. Independent-Samples T-Test
- Scenario: Comparing test scores between male and female students.
- Output: A p-value of 0.03 indicates a significant difference in scores.
2. Chi-Square Test
- Scenario: Examining the relationship between gender and voting preference.
- Output: A p-value of 0.01 suggests a significant association.
3. Correlation Analysis
- Scenario: Assessing the relationship between study hours and exam scores.
- Output: A p-value of 0.04 indicates a significant positive correlation.
Common Misconceptions About Statistical Significance
1. Statistical vs. Practical Significance
- Statistical significance does not always imply practical relevance.
- Example: A statistically significant difference in weight loss might only be 0.5 kg, which may not be meaningful in real life.
2. High Sample Size Bias
- Large samples can produce statistically significant results even for trivial effects.
3. p-value Misinterpretation
- A p-value of 0.05 does not mean there is a 95% chance the result is true. It reflects the probability of observing the results if the null hypothesis is true.
Tips for Beginners Using SPSS
1. Learn the Basics
- Familiarize yourself with SPSS’s interface and functionalities through online tutorials.
2. Understand Your Data
- Know the types of variables and their appropriate tests.
3. Practice Regularly
- Use sample datasets to run different analyses and interpret outputs.
4. Consult Resources
- Refer to books like “Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics” by Andy Field for in-depth understanding.
5. Seek Expert Help
- Collaborate with instructors, peers, or professional SPSS tutors to clarify doubts.
Advanced Concepts Related to Statistical Significance
1. Effect Size
- Measures the magnitude of the difference or relationship.
- Common metrics include Cohen’s d, R-squared, and eta-squared.
2. Confidence Intervals
- Provide a range of values within which the true effect is likely to lie.
- Example: A 95% confidence interval of [2.5, 5.0] indicates high precision.
3. Multiple Comparisons
- Adjust p-values using methods like Bonferroni correction to account for multiple tests.
Benefits of Understanding Statistical Significance in SPSS
1. Improved Research Quality
- Accurate interpretation of results enhances the validity of research.
2. Efficient Decision-Making
- Informed decisions based on reliable data.
3. Enhanced Academic Performance
- Clear and precise reporting of findings impresses evaluators.
4. Career Advancement
- Proficiency in SPSS is a valuable skill for roles in data analysis, research, and academia.
Conclusion
Understanding Statistical Significance in SPSS: A Beginner’s Guide underscores the importance of mastering this critical concept. By following the steps and strategies outlined in this guide, students can confidently analyze data, interpret results, and produce high-quality research. With practice and the right resources, navigating statistical significance in SPSS becomes an achievable and rewarding skill.
Needs help with similar assignment?
We are available 24x7 to deliver the best services and assignment ready within 3-4 hours? Order a custom-written, plagiarism-free paper