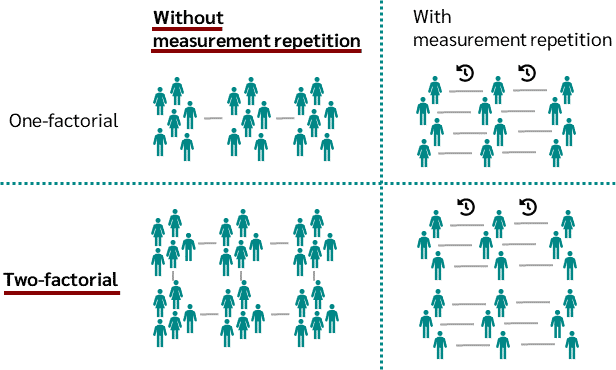Hire an Expert to Do Your SPSS Assignment|2025
/in SPSS Articles /by BesttutorHire an expert to do your SPSS assignment and get accurate, professional solutions tailored to your needs. Save time and achieve better results with reliable SPSS assistance today!
In today’s data-driven world, statistical analysis plays a crucial role in various fields such as psychology, healthcare, education, business, and social sciences. Among the most commonly used statistical software programs is SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences), which is widely regarded as one of the most user-friendly tools for performing a variety of statistical analyses. However, mastering SPSS can be a daunting task for students, especially when faced with complex assignments that require a deep understanding of both the software and statistical concepts.
This is where expert help comes into play. If you’re struggling with your SPSS assignments, hiring a professional to do the work for you can be a game-changer. GetSPSSHelp.com is one of the most reputable platforms where students can get high-quality assistance from experienced SPSS experts. This guide will walk you through the reasons why hiring an expert to do your SPSS assignment is the best decision you can make and why GetSPSSHelp.com is the top choice for students worldwide.
Why Hire an Expert to Do Your SPSS Assignment?
SPSS is a powerful tool used for a variety of statistical tasks, including descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, correlation analysis, regression analysis, and hypothesis testing, among others. While the software itself is highly effective, using it correctly requires a solid understanding of statistical principles and data analysis techniques. Many students often find it challenging to navigate the complexities of SPSS, which can lead to confusion, mistakes, and poor academic performance. Here’s why hiring an expert is a smart choice:
Expertise in Statistical Methods
SPSS assignments often require students to apply various statistical methods, such as t-tests, ANOVA, regression analysis, and chi-square tests. These concepts can be difficult to grasp, especially if you’re not familiar with statistical theory or the nuances of the software. A qualified SPSS expert has the knowledge and experience to handle complex statistical analyses efficiently. Whether you’re working on hypothesis testing, correlation analysis, or data cleaning, an expert will be able to guide you through the process and ensure your results are accurate and reliable.
Save Time and Reduce Stress
One of the main reasons students seek professional help with their SPSS assignments is to save time. SPSS assignments can be time-consuming, especially if you have a tight deadline or multiple assignments to complete. Hiring an expert allows you to focus on other aspects of your studies while the expert handles the technical aspects of data analysis. This can help reduce the stress associated with assignments and allow you to balance your academic responsibilities more effectively.
High-Quality and Accurate Results
Accuracy is paramount in statistical analysis. Even small errors in data analysis can lead to incorrect conclusions and poor grades. An expert SPSS analyst ensures that your analysis is conducted correctly, following the best practices and methodologies. This guarantees that the results you submit are of the highest quality and that your assignment meets the academic standards set by your instructors.
Customization According to Your Needs
Every SPSS assignment is unique, and sometimes, students have specific requirements or guidelines provided by their instructors. Experts at GetSPSSHelp.com work closely with students to ensure that the assignment is customized to meet their individual needs. Whether it’s a specific statistical test, a unique dataset, or specific formatting requirements, professionals can tailor the work according to your preferences.
Learn from Experts
When you hire an expert to do your SPSS assignment, you not only get the completed work, but you also have the opportunity to learn from it. Professionals provide detailed explanations of the analysis process, helping you understand the logic behind each step, how to interpret the results, and how to apply these skills to future assignments. This learning experience can be invaluable for your academic growth and will equip you with the tools you need to succeed in future SPSS tasks.
Why Choose GetSPSSHelp.com?
There are several platforms where you can hire an expert for SPSS assignments, but GetSPSSHelp.com stands out as one of the best. Below are the key reasons why GetSPSSHelp.com is the preferred choice for students around the world.
Experienced and Qualified Experts
At GetSPSSHelp.com, you’ll find a team of experienced SPSS experts with advanced degrees in statistics, data science, and related fields. These professionals have extensive knowledge of SPSS and can perform a wide range of statistical analyses with precision. Whether you need help with a basic descriptive statistics assignment or more advanced tasks like multiple regression or factor analysis, the experts at GetSPSSHelp.com have the skills and knowledge to deliver high-quality results.
Timely Delivery
Meeting deadlines is crucial in academia, and GetSPSSHelp.com understands the importance of timely submission. The platform has a track record of delivering assignments on time, even under tight deadlines. When you hire an expert from GetSPSSHelp.com, you can be confident that your SPSS assignment will be completed and delivered to you within the specified time frame. This gives you peace of mind and allows you to submit your work on time without the stress of last-minute rushing.
Affordable Pricing
One of the main concerns students have when hiring experts for their assignments is the cost. GetSPSSHelp.com offers affordable pricing options that fit within a student’s budget. The platform provides high-quality work at competitive rates, ensuring that students can access professional help without breaking the bank. Additionally, there are various discounts and offers available, making the service even more affordable for students.
24/7 Customer Support
GetSPSSHelp.com offers round-the-clock customer support to assist students with any questions or concerns. Whether you need clarification on the progress of your assignment, have specific requirements, or simply want an update, the customer support team is always available to help. This level of support ensures that you have a seamless experience from start to finish.
Confidentiality and Plagiarism-Free Work
At GetSPSSHelp.com, confidentiality is a top priority. The platform ensures that all personal information and assignment details are kept secure and never shared with third parties. Furthermore, all work is 100% original, and the experts at GetSPSSHelp.com follow strict anti-plagiarism policies. You can be assured that the work you receive is completely unique and tailored to your specific requirements.
Comprehensive SPSS Services
Whether you need help with data entry, cleaning, analysis, or report writing, GetSPSSHelp.com provides comprehensive SPSS services that cover every aspect of your assignment. The platform’s experts are proficient in all types of SPSS analyses, including:
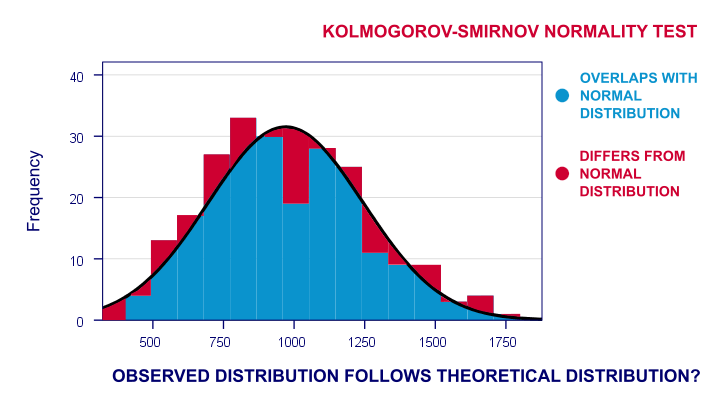
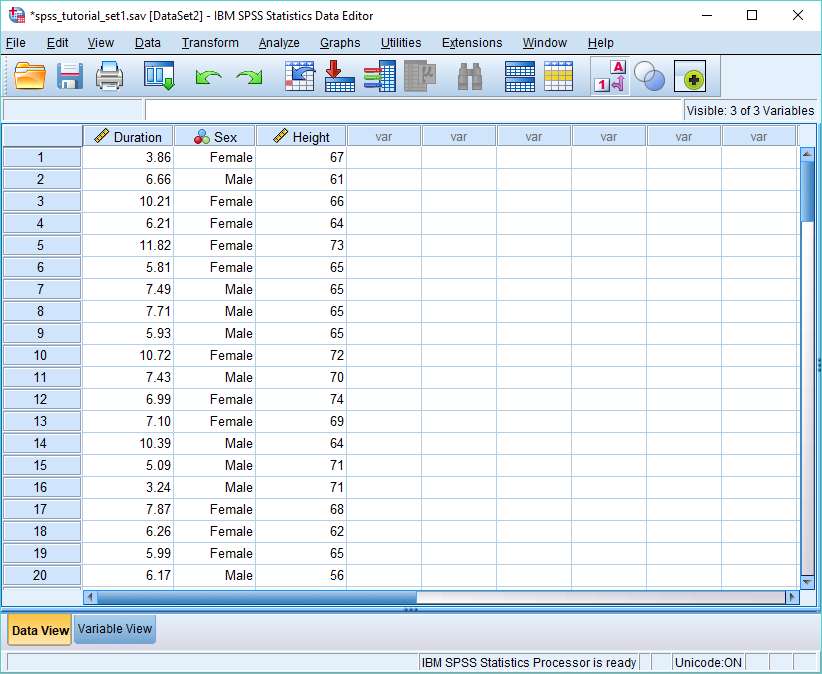
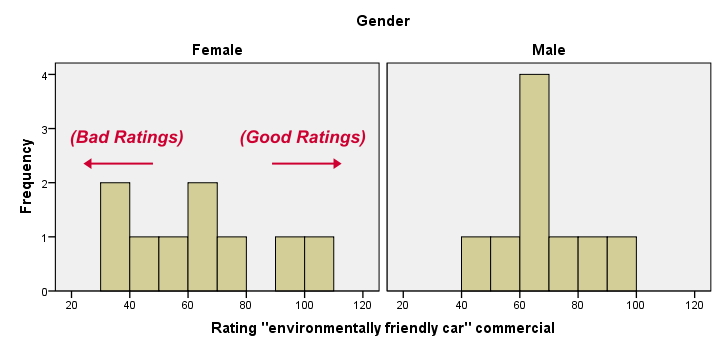
- Descriptive Statistics
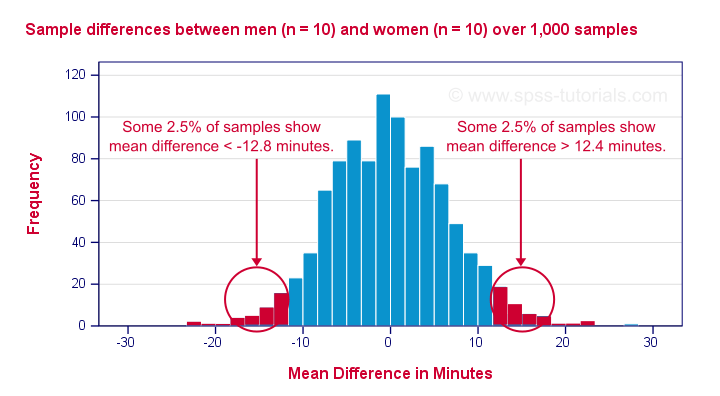
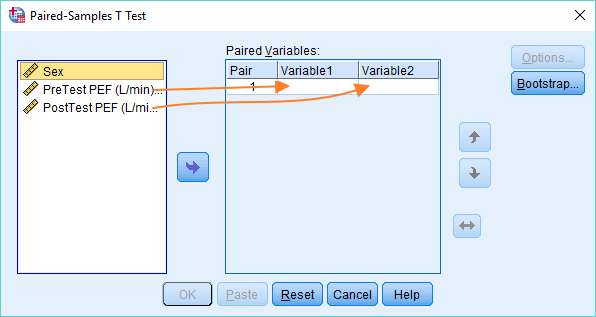
- T-tests (One-sample, Independent, and Paired)
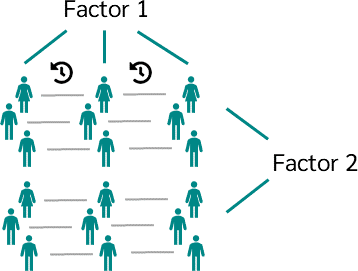
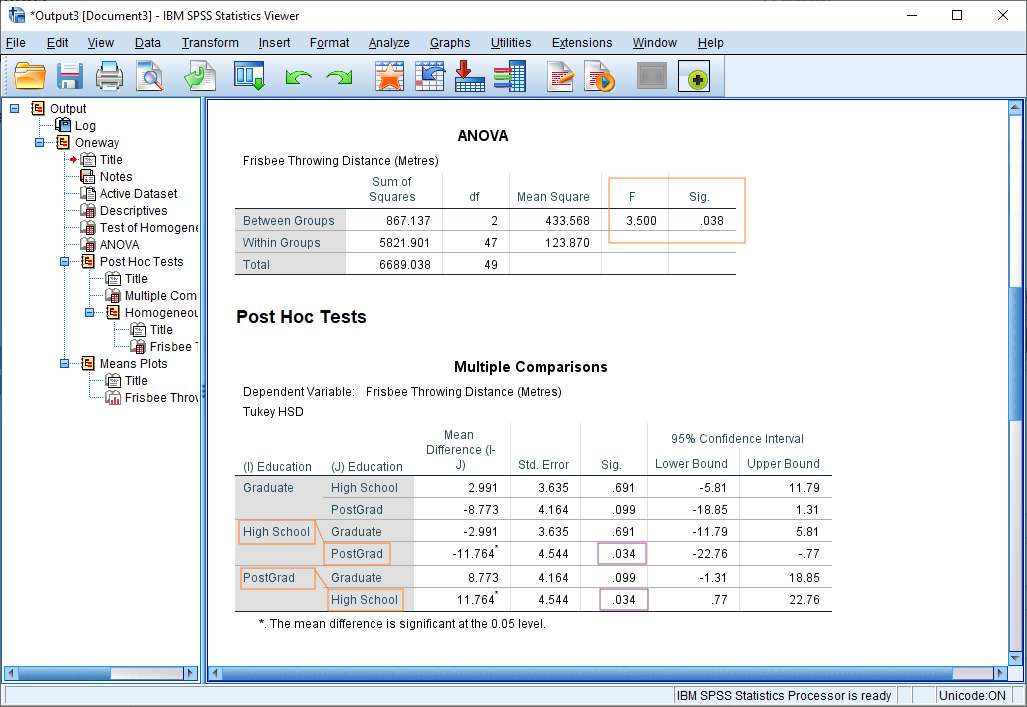
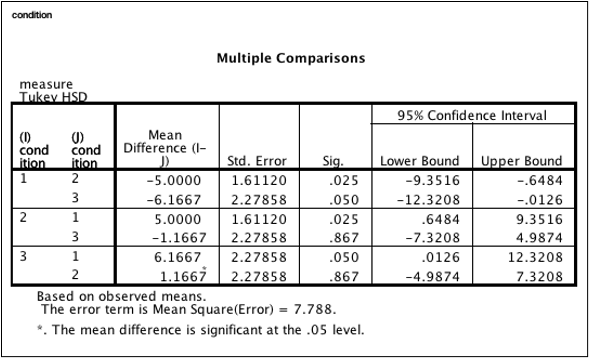
- ANOVA (One-way, Two-way, Repeated Measures)
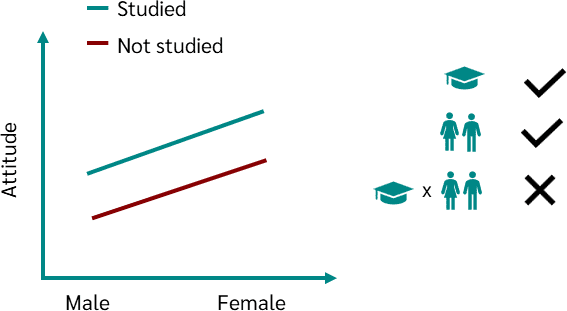
- Regression Analysis (Linear, Multiple)
- Correlation Analysis
- Factor Analysis
- Chi-square Tests
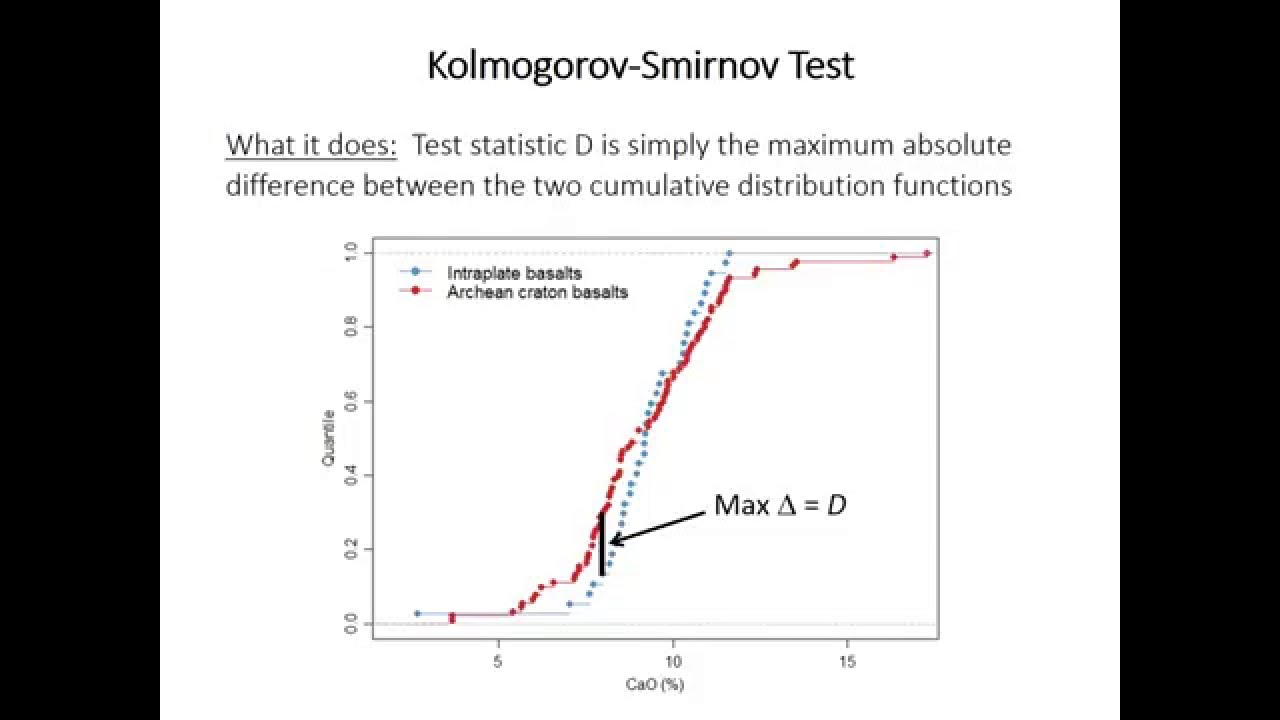
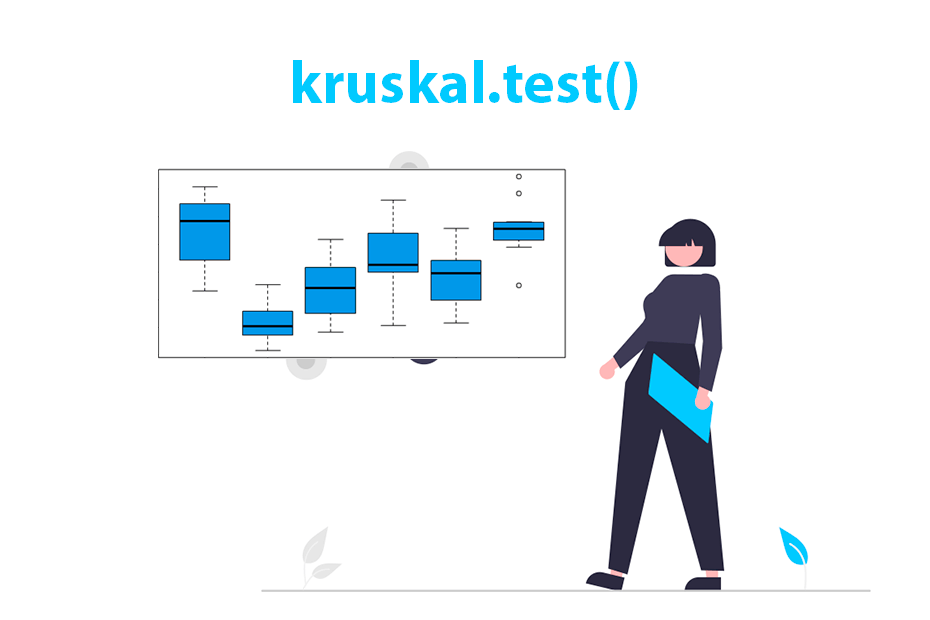
- Non-parametric Tests (e.g., Mann-Whitney U Test, Kruskal-Wallis Test)
No matter how complex or advanced your SPSS assignment is, the experts at GetSPSSHelp.com have the skills and knowledge to assist you.
High Customer Satisfaction
GetSPSSHelp.com has built a reputation for providing excellent service to students worldwide. The platform has a large base of satisfied customers who have benefited from the expert help they’ve received. Positive reviews and testimonials from students attest to the quality of the work, timely delivery, and exceptional customer service provided by the platform.
How to Get Help with Your SPSS Assignment from GetSPSSHelp.com
Getting help with your SPSS assignment from GetSPSSHelp.com is quick and easy. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to place an order:
- Visit the Website: Go to GetSPSSHelp.com to get started.
- Submit Your Assignment Details: Fill out the online form with the details of your SPSS assignment, including the type of analysis, dataset, specific requirements, and deadline.
- Get a Quote: Once you submit your details, the platform will provide you with an instant quote based on the complexity and length of your assignment.
- Make Payment: If you’re satisfied with the quote, proceed with making the payment. GetSPSSHelp.com offers secure payment options to ensure that your transaction is safe and hassle-free.
- Receive Your Completed Assignment: Once the expert has completed your assignment, you will receive the final work. You can request revisions if needed, ensuring that the work meets your expectations.
- Submit Your Work: After reviewing the work, you can submit your SPSS assignment with confidence.
Conclusion
SPSS assignments can be challenging, especially if you’re not familiar with the software or the statistical methods required. Hiring an expert to do your SPSS assignment is a smart decision that can save you time, reduce stress, and ensure that your work is accurate and high-quality. GetSPSSHelp.com stands out as the best platform for hiring experienced SPSS experts who can handle any statistical analysis task. With their timely delivery, affordable pricing, and exceptional customer support, GetSPSSHelp.com is the ideal choice for students looking for professional SPSS assistance. Don’t let your SPSS assignments overwhelm you—get expert help today and submit your best work with confidence!
Needs help with similar assignment?
We are available 24x7 to deliver the best services and assignment ready within 3-4 hours? Order a custom-written, plagiarism-free paper